Generalized vs. stimulus-specific learned fear differentially modifies stimulus encoding in primary sensory cortex of awake rats
- PMID: 21918001
- PMCID: PMC3234083
- DOI: 10.1152/jn.00721.2011
Generalized vs. stimulus-specific learned fear differentially modifies stimulus encoding in primary sensory cortex of awake rats
Abstract
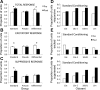
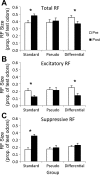
Experience shapes both central olfactory system function and odor perception. In piriform cortex, odor experience appears critical for synthetic processing of odor mixtures, which contributes to perceptual learning and perceptual acuity, as well as contributing to memory for events and/or rewards associated with odors. Here, we examined the effect of odor fear conditioning on piriform cortical single-unit responses to the learned aversive odor, as well as its effects on similar (overlapping mixtures) in freely moving rats. We found that odor-evoked fear responses were training paradigm dependent. Simple association of a condition stimulus positive (CS+) odor with foot shock (unconditioned stimulus) led to generalized fear (cue-evoked freezing) to similar odors. However, after differential conditioning, which included trials where a CS- odor (a mixture overlapping with the CS+) was not paired with shock, freezing responses were CS+ odor specific and less generalized. Pseudoconditioning led to no odor-evoked freezing. These differential levels of stimulus control over freezing were associated with different training-induced changes in single-unit odor responses in anterior piriform cortex (aPCX). Both simple and differential conditioning induced a significant decrease in aPCX single-unit spontaneous activity compared with pretraining levels while pseudoconditioning did not. Simple conditioning enhanced mean receptive field size (breadth of tuning) of the aPCX units, while differential conditioning reduced mean receptive field size. These results suggest that generalized fear is associated with an impairment of olfactory cortical discrimination. Furthermore, changes in sensory processing are dependent on the nature of training and can predict the stimulus-controlled behavioral outcome of the training.
Figures




References
-
- Armony JL, Servan-Schreiber D, Romanski LM, Cohen JD, LeDoux JE. Stimulus generalization of fear responses: effects of auditory cortex lesions in a computational model and in rats. Cereb Cortex 7: 157–165, 1997 - PubMed
-
- Brennan P, Kaba H, Keverne EB. Olfactory recognition: a simple memory system. Science 250: 1223–1226, 1990 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

