Itaconic acid is a mammalian metabolite induced during macrophage activation
- PMID: 21919507
- PMCID: PMC3216473
- DOI: 10.1021/ja2070889
Itaconic acid is a mammalian metabolite induced during macrophage activation
Abstract
Itaconic acid (ITA), or methylenesuccinic acid, is not generally classified as a mammalian metabolite. Using NMR-based metabolomics and (13)C-labeling, we have detected ITA in both macrophage-like VM-M3 and RAW 264.7 tumor cell lines as well as stimulated and unstimulated primary murine macrophages. Macrophage activation by addition of lipopolysaccharide and IFN-γ markedly increased ITA production and secretion. Crude cell extracts synthesize ITA via decarboxylation of cis-aconitate, indicative of a novel mammalian cis-aconitic decarboxylase activity. Our results highlight a previously unidentified biosynthetic pathway related to TCA cycle metabolism in mammalian cells and a novel metabolite that likely plays a role in macrophage-based immune response.
Figures

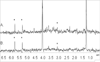
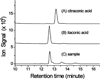

 )) and [U-13C]glucose (B and C) if the cis-aconitic decarboxylase (cADC) pathway is active. [U-13C]glucose enters glycolysis and results in 13C3-pyruvate, which can enter the TCA cycle as 13C2-acetyl CoA through pyruvate dehydrogenase (PDH), or as 13C3-oxaloacetate through pyruvate carboxylase (PC). The isotopologuess of ITA synthesized by this pathway should be predominantely 13C1 (PDH flux only, (B,
)) and [U-13C]glucose (B and C) if the cis-aconitic decarboxylase (cADC) pathway is active. [U-13C]glucose enters glycolysis and results in 13C3-pyruvate, which can enter the TCA cycle as 13C2-acetyl CoA through pyruvate dehydrogenase (PDH), or as 13C3-oxaloacetate through pyruvate carboxylase (PC). The isotopologuess of ITA synthesized by this pathway should be predominantely 13C1 (PDH flux only, (B,  )) or 13C4 (both PC and PDH flux, (C,
)) or 13C4 (both PC and PDH flux, (C,  )). (D) Comparison of isotopologues of itaconic acid, citric acid and aconitate in VM-M3 cells after incubation with [U-13C]glucose: isotopologuess resulting from PDH flux
)). (D) Comparison of isotopologues of itaconic acid, citric acid and aconitate in VM-M3 cells after incubation with [U-13C]glucose: isotopologuess resulting from PDH flux  , or PC/PDH flux [///].
, or PC/PDH flux [///].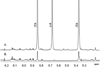
References
-
- Bentley R, Thiessen CP. Science. 1955;122:330. - PubMed
-
- Yu C, Cao Y, Zou H, Xian M. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2011;89:573–583. - PubMed
-
- Okabe M, Lies D, Kanamasa S. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2009;84:597–606. - PubMed
-
- Shin J, Yang J, Jeon B, Yoon YJ, Cho S, Kang Y, Ryu DH, Hwang G. J. Proteome Res. 2011;10:2238–2247. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

