The snail repressor inhibits release, not elongation, of paused Pol II in the Drosophila embryo
- PMID: 21920753
- PMCID: PMC3186076
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cub.2011.08.019
The snail repressor inhibits release, not elongation, of paused Pol II in the Drosophila embryo
Abstract
The development of the precellular Drosophila embryo is characterized by exceptionally rapid transitions in gene activity, with broadly distributed maternal regulatory gradients giving way to precise on/off patterns of gene expression within a one-hour window, between two and three hours after fertilization [1]. Transcriptional repression plays a pivotal role in this process, delineating sharp expression patterns (e.g., pair-rule stripes) within broad domains of gene activation. As many as 20 different sequence-specific repressors have been implicated in this process, yet the mechanisms by which they silence gene expression have remained elusive [2]. Here we report the development of a method for the quantitative visualization of transcriptional repression. We focus on the Snail repressor, which establishes the boundary between the presumptive mesoderm and neurogenic ectoderm [3]. We find that elongating Pol II complexes complete transcription after the onset of Snail repression. As a result, moderately sized genes (e.g., the 22 kb sog locus) are fully silenced only after tens of minutes of repression. We propose that this "repression lag" imposes a severe constraint on the regulatory dynamics of embryonic patterning and further suggest that posttranscriptional regulators, like microRNAs, are required to inhibit unwanted transcripts produced during protracted periods of gene silencing.
Copyright © 2011 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures
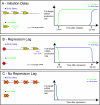


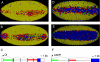
Comment in
-
Transcriptional repressors: shutting off gene expression at the source affects developmental dynamics.Curr Biol. 2011 Oct 25;21(20):R859-60. doi: 10.1016/j.cub.2011.09.022. Curr Biol. 2011. PMID: 22032193
Similar articles
-
Short-range transcriptional repressors mediate both quenching and direct repression within complex loci in Drosophila.Genes Dev. 1996 Mar 15;10(6):700-10. doi: 10.1101/gad.10.6.700. Genes Dev. 1996. PMID: 8598297
-
The Snail repressor positions Notch signaling in the Drosophila embryo.Development. 2002 Apr;129(7):1785-93. doi: 10.1242/dev.129.7.1785. Development. 2002. PMID: 11923213
-
Transcriptional repressors: shutting off gene expression at the source affects developmental dynamics.Curr Biol. 2011 Oct 25;21(20):R859-60. doi: 10.1016/j.cub.2011.09.022. Curr Biol. 2011. PMID: 22032193
-
Threshold responses to the dorsal regulatory gradient and the subdivision of primary tissue territories in the Drosophila embryo.Curr Opin Genet Dev. 1996 Aug;6(4):416-23. doi: 10.1016/s0959-437x(96)80062-1. Curr Opin Genet Dev. 1996. PMID: 8791536 Review.
-
Control of Drosophila embryo patterning by transcriptional co-regulators.Exp Cell Res. 2014 Feb 1;321(1):47-57. doi: 10.1016/j.yexcr.2013.10.010. Epub 2013 Oct 22. Exp Cell Res. 2014. PMID: 24157250 Review.
Cited by
-
Complex cis-regulatory landscape of the insulin receptor gene underlies the broad expression of a central signaling regulator.Development. 2016 Oct 1;143(19):3591-3603. doi: 10.1242/dev.138073. Development. 2016. PMID: 27702787 Free PMC article.
-
Modulation of temporal dynamics of gene transcription by activator potency in the Drosophila embryo.Development. 2015 Nov 1;142(21):3781-90. doi: 10.1242/dev.126946. Epub 2015 Sep 22. Development. 2015. PMID: 26395487 Free PMC article.
-
Rtf1 Transcriptionally Regulates Neonatal and Adult Cardiomyocyte Biology.J Cardiovasc Dev Dis. 2023 May 20;10(5):221. doi: 10.3390/jcdd10050221. J Cardiovasc Dev Dis. 2023. PMID: 37233188 Free PMC article.
-
Shadow enhancers modulate distinct transcriptional parameters that differentially effect downstream patterning events.Development. 2022 Nov 1;149(21):dev200940. doi: 10.1242/dev.200940. Epub 2022 Nov 1. Development. 2022. PMID: 36264246 Free PMC article.
-
Mitosis-associated repression in development.Genes Dev. 2016 Jul 1;30(13):1503-8. doi: 10.1101/gad.281188.116. Genes Dev. 2016. PMID: 27401553 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Lawrence PA, Struhl G. Morphogens, Compartments and Pattern: Lessons from Drosophila? Cell. 1992;85:951–961. - PubMed
-
- Kosman D, Ip YT, Levine M, Arora K. Establishment of the mesoderm-neuroectoderm boundary in the Drosophila embryo. Science. 1991;254:118–22. - PubMed
-
- Boulay JL, Dennefeld C, Alberga A. The Drosophila developmental gene snail encodes a protein with nucleic acid binding fingers. Nature. 1987;330:395–398. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

