Hypoxia-inducible transcription factors stabilization in the thick ascending limb protects against ischemic acute kidney injury
- PMID: 21921145
- PMCID: PMC3279994
- DOI: 10.1681/ASN.2010121249
Hypoxia-inducible transcription factors stabilization in the thick ascending limb protects against ischemic acute kidney injury
Abstract
Hypoxia-inducible transcription factors (HIF) protect cells against oxygen deprivation, and HIF stabilization before ischemia mitigates tissue injury. Because ischemic acute kidney injury (AKI) often involves the thick ascending limb (TAL), modulation of HIF in this segment may be protective. Here, we generated mice with targeted TAL deletion of the von Hippel-Lindau protein (Vhl), which mediates HIF degradation under normoxia, using Tamm-Horsfall protein (Thp)-driven Cre expression. These mice showed strong expression of HIF-1α in TALs but no changes in kidney morphology or function under control conditions. Deficiency of Vhl in the TAL markedly attenuated proximal tubular injury and preserved TAL function following ischemia-reperfusion, which may be partially a result of enhanced expression of glycolytic enzymes and lactate metabolism. These results highlight the importance of the thick ascending limb in the pathogenesis of AKI and suggest that pharmacologically targeting the HIF system may have potential to prevent and mitigate AKI.
Figures
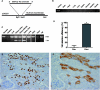
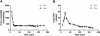
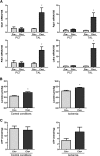
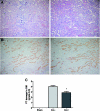


References
-
- Thakar CV, Christianson A, Freyberg R, Almenoff P, Render ML: Incidence and outcomes of acute kidney injury in intensive care units: A Veterans Administration study. Crit Care Med 37: 2552–2558, 2009 - PubMed
-
- Brezis M, Rosen S: Hypoxia of the renal medulla–its implications for disease. N Engl J Med 332: 647–655, 1995 - PubMed
-
- Eckardt KU, Bernhardt WM, Weidemann A, Warnecke C, Rosenberger C, Wiesener MS, Willam C: Role of hypoxia in the pathogenesis of renal disease. Kidney Int Suppl: S46–S51, 2005 - PubMed
-
- Heyman SN, Rosenberger C, Rosen S: Experimental ischemia-reperfusion: Biases and myths-the proximal vs. distal hypoxic tubular injury debate revisited. Kidney Int 77: 9–16, 2010 - PubMed
-
- Heyman SN, Shina A, Brezis M, Rosen S: Proximal tubular injury attenuates outer medullary hypoxic damage: studies in perfused rat kidneys. Exp Nephrol 10: 259–266, 2002 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

