Information transduction capacity of noisy biochemical signaling networks
- PMID: 21921160
- PMCID: PMC3895446
- DOI: 10.1126/science.1204553
Information transduction capacity of noisy biochemical signaling networks
Abstract
Molecular noise restricts the ability of an individual cell to resolve input signals of different strengths and gather information about the external environment. Transmitting information through complex signaling networks with redundancies can overcome this limitation. We developed an integrative theoretical and experimental framework, based on the formalism of information theory, to quantitatively predict and measure the amount of information transduced by molecular and cellular networks. Analyzing tumor necrosis factor (TNF) signaling revealed that individual TNF signaling pathways transduce information sufficient for accurate binary decisions, and an upstream bottleneck limits the information gained via multiple integrated pathways. Negative feedback to this bottleneck could both alleviate and enhance its limiting effect, despite decreasing noise. Bottlenecks likewise constrain information attained by networks signaling through multiple genes or cells.
Figures

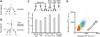
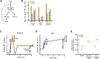


Comment in
-
Cell signaling. Every bit counts.Science. 2011 Oct 21;334(6054):321-2. doi: 10.1126/science.1213834. Science. 2011. PMID: 22021849 No abstract available.
References
-
- Rosenfeld N, Young JW, Alon U, Swain PS, Elowitz MB. Gene regulation at the single-cell level. Science. 2005;307:1962. - PubMed
-
- Blake WJ, Cantor KAMCR, Collins JJ. Noise in eukaryotic gene expression. Nature. 2003;422:633. - PubMed
-
- Elowitz MB, Levine AJ, Siggia ED, Swain PS. Stochastic gene expression in a single cell. Science. 2002;297:1183. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

