Functional impairment of skeletal muscle oxidative metabolism during knee extension exercise after bed rest
- PMID: 21921243
- PMCID: PMC3233880
- DOI: 10.1152/japplphysiol.01380.2010
Functional impairment of skeletal muscle oxidative metabolism during knee extension exercise after bed rest
Abstract
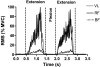
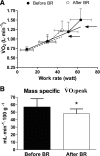
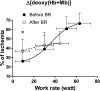
A functional evaluation of skeletal muscle oxidative metabolism during dynamic knee extension (KE) incremental exercises was carried out following a 35-day bed rest (BR) (Valdoltra 2008 BR campaign). Nine young male volunteers (age: 23.5 ± 2.2 yr; mean ± SD) were evaluated. Pulmonary gas exchange, heart rate and cardiac output (by impedance cardiography), skeletal muscle (vastus lateralis) fractional O(2) extraction, and brain (frontal cortex) oxygenation (by near-infrared spectroscopy) were determined during incremental KE. Values at exhaustion were considered "peak". Peak heart rate (147 ± 18 beats/min before vs. 146 ± 17 beats/min after BR) and peak cardiac output (17.8 ± 3.3 l/min before vs. 16.1 ± 1.8 l/min after BR) were unaffected by BR. As expected, brain oxygenation did not decrease during KE. Peak O(2) uptake was lower after vs. before BR, both when expressed as liters per minute (0.99 ± 0.17 vs. 1.26 ± 0.27) and when normalized per unit of quadriceps muscle mass (46.5 ± 6.4 vs. 56.9 ± 11.0 ml·min(-1)·100 g(-1)). Skeletal muscle peak fractional O(2) extraction, expressed as a percentage of the maximal values obtained during a transient limb ischemia, was lower after (46.3 ± 12.1%) vs. before BR (66.5 ± 11.2%). After elimination, by the adopted exercise protocol, of constraints related to cardiovascular O(2) delivery, a decrease in peak O(2) uptake and muscle peak capacity of fractional O(2) extraction was found after 35 days of BR. These findings suggest a substantial impairment of oxidative function at the muscle level, "downstream" with respect to bulk blood flow to the exercising muscles, that is possibly at the level of blood flow distribution/O(2) utilization inside the muscle, peripheral O(2) diffusion, and intracellular oxidative metabolism.
Figures
Similar articles
-
PlanHab* : hypoxia does not worsen the impairment of skeletal muscle oxidative function induced by bed rest alone.J Physiol. 2018 Aug;596(15):3341-3355. doi: 10.1113/JP275605. Epub 2018 Apr 17. J Physiol. 2018. PMID: 29665013 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Role of skeletal muscles impairment and brain oxygenation in limiting oxidative metabolism during exercise after bed rest.J Appl Physiol (1985). 2010 Jul;109(1):101-11. doi: 10.1152/japplphysiol.00782.2009. Epub 2010 Apr 15. J Appl Physiol (1985). 2010. PMID: 20395541
-
Separate and combined effects of a 10-d exposure to hypoxia and inactivity on oxidative function in vivo and mitochondrial respiration ex vivo in humans.J Appl Physiol (1985). 2016 Jul 1;121(1):154-63. doi: 10.1152/japplphysiol.00832.2015. Epub 2016 May 19. J Appl Physiol (1985). 2016. PMID: 27197861
-
Lack of functional effects of neuromuscular electrical stimulation on skeletal muscle oxidative metabolism in healthy humans.J Appl Physiol (1985). 2012 Oct;113(7):1101-9. doi: 10.1152/japplphysiol.01627.2011. Epub 2012 Aug 16. J Appl Physiol (1985). 2012. PMID: 22898549
-
Insights into central and peripheral factors affecting the "oxidative performance" of skeletal muscle in aging.Eur J Appl Physiol. 2007 Jul;100(5):571-9. doi: 10.1007/s00421-006-0371-x. Epub 2006 Dec 22. Eur J Appl Physiol. 2007. PMID: 17186297 Clinical Trial.
Cited by
-
PlanHab* : hypoxia does not worsen the impairment of skeletal muscle oxidative function induced by bed rest alone.J Physiol. 2018 Aug;596(15):3341-3355. doi: 10.1113/JP275605. Epub 2018 Apr 17. J Physiol. 2018. PMID: 29665013 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Effects of 21 days of bed rest and whey protein supplementation on plantar flexor muscle fatigue resistance during repeated shortening contractions.Eur J Appl Physiol. 2020 May;120(5):969-983. doi: 10.1007/s00421-020-04333-5. Epub 2020 Mar 4. Eur J Appl Physiol. 2020. PMID: 32130485 Free PMC article.
-
Mitochondrial Adaptations in Elderly and Young Men Skeletal Muscle Following 2 Weeks of Bed Rest and Rehabilitation.Front Physiol. 2019 May 1;10:474. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2019.00474. eCollection 2019. Front Physiol. 2019. PMID: 31118897 Free PMC article.
-
Skeletal muscle oxygen uptake in obese patients: functional evaluation by knee-extension exercise.Eur J Appl Physiol. 2013 Aug;113(8):2125-32. doi: 10.1007/s00421-013-2647-2. Epub 2013 Apr 19. Eur J Appl Physiol. 2013. PMID: 23604706
-
Impact of 60 days of 6° head down tilt bed rest on muscular oxygen uptake and heart rate kinetics: efficacy of a reactive sledge jump countermeasure.Eur J Appl Physiol. 2018 Sep;118(9):1885-1901. doi: 10.1007/s00421-018-3915-y. Epub 2018 Jun 26. Eur J Appl Physiol. 2018. PMID: 29946969
References
-
- Andersen P, Adams RP, SjØgaard G, Thorboe A, Saltin B. Dynamic knee extension as model for study of isolated exercising muscle in humans. J Appl Physiol 59: 1647–1653, 1985 - PubMed
-
- Beaver WL, Wasserman K, Whipp BJ. A new method for detecting anaerobic threshold by gas exchange. J Appl Physiol 60: 2020–2027, 1986 - PubMed
-
- Bloomfield SA. Changes in musculoskeletal structure and function with prolonged bed rest. Med Sci Sports Exerc 29: 197–206, 1997 - PubMed
-
- Borina E, Pellegrino MA, D'Antona G, Bottinelli R. Myosin and actin content of human skeletal muscle fibers following 35 days bed rest. Scand J Med Sci Sports 20: 65–73, 2010 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

