Hydrogen sulfide preconditioning or neutrophil depletion attenuates ischemia-reperfusion-induced mitochondrial dysfunction in rat small intestine
- PMID: 21921289
- PMCID: PMC3345957
- DOI: 10.1152/ajpgi.00413.2010
Hydrogen sulfide preconditioning or neutrophil depletion attenuates ischemia-reperfusion-induced mitochondrial dysfunction in rat small intestine
Abstract
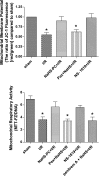
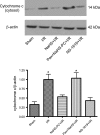
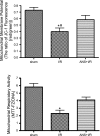
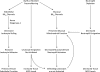
The objectives of this study were to determine whether neutrophil depletion with anti-neutrophil serum (ANS) or preconditioning with the hydrogen sulfide (H(2)S) donor NaHS (NaHS-PC) 24 h prior to ischemia-reperfusion (I/R) would prevent postischemic mitochondrial dysfunction in rat intestinal mucosa and, if so, whether calcium-activated, large conductance potassium (BK(Ca)) channels were involved in this protective effect. I/R was induced by 45-min occlusion of the superior mesenteric artery followed by 60-min reperfusion in rats preconditioned with NaHS (NaHS-PC) or a BK(Ca) channel activator (NS-1619-PC) 24 h earlier or treated with ANS. Mitochondrial function was assessed by measuring mitochondrial membrane potential, mitochondrial dehydrogenase function, and cytochrome c release. Mucosal myeloperoxidase (MPO) and TNF-α levels were also determined, as measures of postischemic inflammation. BK(Ca) expression in intestinal mucosa was detected by immunohistochemistry and Western blotting. I/R induced mitochondrial dysfunction and increased tissue MPO and TNF-α levels. Although mitochondrial dysfunction was attenuated by NaHS-PC or NS-1619-PC, the postischemic increases in mucosal MPO and TNF-α levels were not. The protective effect of NaHS-PC or NS-1619-PC on postischemic mitochondrial function was abolished by coincident treatment with BK(Ca) channel inhibitors. ANS prevented the I/R-induced increase in tissue MPO levels and reversed mitochondrial dysfunction. These data indicate that neutrophils play an essential role in I/R-induced mucosal mitochondrial dysfunction. In addition, NaHS-PC prevents postischemic mitochondrial dysfunction (but not inflammation) by a BK(Ca) channel-dependent mechanism.
Figures



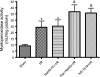

References
-
- Boehning D, Snyder S. Novel neural modulators. Annu Rev Neurosci 26: 105–131, 2003 - PubMed
-
- Cho J, Won K, Wu D, Soong Y, Liu S, Szeto HH, Hong MK. Potent mitochondria-targeted peptides reduce myocardial infarction in rats. Coron Artery Dis 18: 215–220, 2007 - PubMed
-
- Cooper D, Russell J, Chitman KD, Williams MC, Wolf RE, Granger DN. Leukocyte dependence of platelet adhesion in postcapillary venules. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol 286: H1895–H1900, 2004 - PubMed
-
- Douglas RM, Lai JC, Bian S, Cummins L, Moczydlowski E, Haddad GG. The calcium-sensitive large-conductance potassium channel (BK/MAXI K) is present in the inner mitochondrial membrane of rat brain. Neuroscience 139: 1249–1261, 2006 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

