In situ proliferation and differentiation of macrophages in dental pulp
- PMID: 21922246
- PMCID: PMC3204101
- DOI: 10.1007/s00441-011-1231-5
In situ proliferation and differentiation of macrophages in dental pulp
Abstract
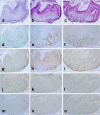
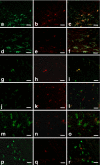
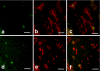
The presence of macrophages in dental pulp is well known. However, whether these macrophages proliferate and differentiate in the dental pulp in situ, or whether they constantly migrate from the blood stream into the dental pulp remains unknown. We have examined and compared the development of dental pulp macrophages in an organ culture system with in vivo tooth organs to clarify the developmental mechanism of these macrophages. The first mandibular molar tooth organs from ICR mice aged between 16 days of gestation (E16) to 5 days postnatally were used for in vivo experiments. Those from E16 were cultured for up to 14 days with or without 10% fetal bovine serum. Dental pulp tissues were analyzed with immunohistochemistry to detect the macrophages and with reverse transcription and the polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR) for the detection of factors related to macrophage development. The growth curves for the in vivo and in vitro cultured cells revealed similar numbers of F4/80-positive macrophages in the dental pulp. RT-PCR analysis indicated the constant expression of myeloid colony-stimulating factor (M-CSF) in both in-vivo- and in-vitro-cultured dental pulp tissues. Anti-M-CSF antibodies significantly inhibited the increase in the number of macrophages in the dental pulp. These results suggest that (1) most of the dental pulp macrophages proliferate and differentiate in the dental pulp without a supply of precursor cells from the blood stream, (2) M-CSF might be a candidate molecule for dental pulp macrophage development, and (3) serum factors might not directly affect the development of macrophages.
Figures




References
-
- Chan J, Leenen PJ, Bertoncello I, Nishikawa SI, Hamilton JA. Macrophage lineage cells in inflammation: characterization by colony-stimulating factor-1 (CSF-1) receptor (c-Fms), ER-MP58, and ER-MP20 (Ly-6C) expression. Blood. 1998;92:1423–1431. - PubMed
-
- Daems WT, Brederoo P. The fine structure and peroxidase activity of resident and exudate peritoneal macrophages in the guinea pig. Adv Exp Med Biol. 1972;15:19–31.
-
- Daems WT, van der Rhee HJ. Peroxidase and catalase in monocytes, macrophages, epithelioid cells and giant cells of the rat. In: van Furth R, editor. Mononuclear phagocytes, functional aspects. The Hague: Nijhoff; 1980. pp. 43–60.
-
- Daems WT, Koerten HK, Soranzo MR. Differences between monocyte-derived and tissue macrophages. Adv Exp Med Biol. 1976;73:27–40. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

