Dll4-Notch signaling as a therapeutic target in tumor angiogenesis
- PMID: 21923938
- PMCID: PMC3195111
- DOI: 10.1186/2045-824X-3-20
Dll4-Notch signaling as a therapeutic target in tumor angiogenesis
Abstract
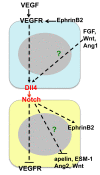
Tumor angiogenesis is an important target for cancer therapy, with most current therapies designed to block the VEGF signaling pathway. However, clinical resistance to anti-VEGF therapy highlights the need for targeting additional tumor angiogenesis signaling pathways. The endothelial Notch ligand Dll4 (delta-like 4) has recently emerged as a critical regulator of tumor angiogenesis and thus as a promising new therapeutic anti-angiogenesis target. Blockade of Dll4-Notch signaling in tumors results in excessive, non-productive angiogenesis with resultant inhibitory effects on tumor growth, even in some tumors that are resistant to anti-VEGF therapies. As Dll4 inhibitors are entering clinical cancer trials, this review aims to provide current perspectives on the function of the Dll4-Notch signaling axis during tumor angiogenesis and as a target for anti-angiogenic cancer therapy.
Figures

Similar articles
-
The Notch ligand Delta-like 4 (DLL4) as a target in angiogenesis-based cancer therapy?Contemp Oncol (Pozn). 2013;17(3):234-7. doi: 10.5114/wo.2013.35588. Epub 2013 Jun 28. Contemp Oncol (Pozn). 2013. PMID: 24596507 Free PMC article. Review.
-
DLL4-Notch signaling mediates tumor resistance to anti-VEGF therapy in vivo.Cancer Res. 2011 Sep 15;71(18):6073-83. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-11-1704. Epub 2011 Jul 29. Cancer Res. 2011. PMID: 21803743
-
Crosstalk of VEGF and Notch pathways in tumour angiogenesis: therapeutic implications.Front Biosci (Landmark Ed). 2009 Jan 1;14(8):3094-110. doi: 10.2741/3438. Front Biosci (Landmark Ed). 2009. PMID: 19273260 Review.
-
Delta-like 4 Notch ligand regulates tumor angiogenesis, improves tumor vascular function, and promotes tumor growth in vivo.Cancer Res. 2007 Dec 1;67(23):11244-53. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-07-0969. Cancer Res. 2007. PMID: 18056450
-
Dll4 blockade potentiates the anti-tumor effects of VEGF inhibition in renal cell carcinoma patient-derived xenografts.PLoS One. 2014 Nov 13;9(11):e112371. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0112371. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 25393540 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Arsenic Trioxide Suppresses Tumor Growth through Antiangiogenesis via Notch Signaling Blockade in Small-Cell Lung Cancer.Biomed Res Int. 2019 Apr 10;2019:4647252. doi: 10.1155/2019/4647252. eCollection 2019. Biomed Res Int. 2019. PMID: 31093499 Free PMC article.
-
PlGF-induced VEGFR1-dependent vascular remodeling determines opposing antitumor effects and drug resistance to Dll4-Notch inhibitors.Sci Adv. 2015 Apr 10;1(3):e1400244. doi: 10.1126/sciadv.1400244. eCollection 2015 Apr. Sci Adv. 2015. PMID: 26601163 Free PMC article.
-
Role of Notch signalling pathway in cancer and its association with DNA methylation.J Genet. 2013 Dec;92(3):667-75. doi: 10.1007/s12041-013-0284-5. J Genet. 2013. PMID: 24371188 Review.
-
Notch as a tumour suppressor.Nat Rev Cancer. 2017 Mar;17(3):145-159. doi: 10.1038/nrc.2016.145. Epub 2017 Feb 3. Nat Rev Cancer. 2017. PMID: 28154375 Review.
-
Single-cell atlas of human pancreatic islet and acinar endothelial cells in health and diabetes.Nat Commun. 2025 Feb 6;16(1):1338. doi: 10.1038/s41467-024-55415-3. Nat Commun. 2025. PMID: 39915484 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

