GM-CSF modulates pulmonary resistance to influenza A infection
- PMID: 21925209
- PMCID: PMC4894852
- DOI: 10.1016/j.antiviral.2011.08.022
GM-CSF modulates pulmonary resistance to influenza A infection
Abstract
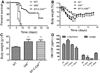
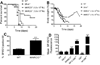
Alveolar type II epithelial or other pulmonary cells secrete GM-CSF that regulates surfactant catabolism and mucosal host defense through its capacity to modulate the maturation and activation of alveolar macrophages. GM-CSF enhances expression of scavenger receptors MARCO and SR-A. The alveolar macrophage SP-R210 receptor binds the surfactant collectin SP-A mediating clearance of respiratory pathogens. The current study determined the effects of epithelial-derived GM-CSF in host resistance to influenza A pneumonia. The results demonstrate that GM-CSF enhanced resistance to infection with 1.9×10(4) ffc of the mouse-adapted influenza A/Puerto Rico/8/34 (PR8) H1N1 strain, as indicated by significant differences in mortality and mean survival of GM-CSF-deficient (GM(-/-)) mice compared to GM(-/-) mice in which GM-CSF is expressed at increased levels. Protective effects of GM-CSF were observed both in mice with constitutive and inducible GM-CSF expression under the control of the pulmonary-specific SFTPC or SCGB1A1 promoters, respectively. Mice that continuously secrete high levels of GM-CSF developed desquamative interstitial pneumonia that impaired long-term recovery from influenza. Conditional expression of optimal GM-CSF levels at the time of infection, however, resulted in alveolar macrophage proliferation and focal lymphocytic inflammation of distal airways. GM-CSF enhanced alveolar macrophage activity as indicated by increased expression of SP-R210 and CD11c. Infection of mice lacking the GM-CSF-regulated SR-A and MARCO receptors revealed that MARCO decreases resistance to influenza in association with increased levels of SP-R210 in MARCO(-/-) alveolar macrophages. In conclusion, GM-CSF enhances early host resistance to influenza. Targeting of MARCO may reinforce GM-CSF-mediated host defense against pathogenic influenza.
Copyright © 2011 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Figures





References
-
- Arora DJ, Tremblay P, Bourgault R, Boileau S. Concentration and purification of influenza virus from allantoic fluid. Anal. Biochem. 1985;144:189–192. - PubMed
-
- Baskin CR, Bielefeldt-Ohmann H, Tumpey TM, Sabourin PJ, Long JP, Garcia-Sastre A, Tolnay AE, Albrecht R, Pyles JA, Olson PH, Aicher LD, Rosenzweig ER, Murali-Krishna K, Clark EA, Kotur MS, Fornek JL, Proll S, Palermo RE, Sabourin CL, Katze MG. Early and sustained innate immune response defines pathology and death in nonhuman primates infected by highly pathogenic influenza virus. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. 2009;106:3455–3460. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

