The noncoding RNA Mistral activates Hoxa6 and Hoxa7 expression and stem cell differentiation by recruiting MLL1 to chromatin
- PMID: 21925392
- PMCID: PMC3176448
- DOI: 10.1016/j.molcel.2011.08.019
The noncoding RNA Mistral activates Hoxa6 and Hoxa7 expression and stem cell differentiation by recruiting MLL1 to chromatin
Retraction in
-
Retraction notice to: The noncoding RNA mistral activates Hoxa6 and Hoxa7 expression and stem cell differentiation by recruiting MLL1 to chromatin.Mol Cell. 2015 Feb 5;57(3):572. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2015.01.032. Mol Cell. 2015. PMID: 25811052 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
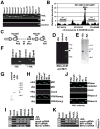
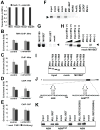
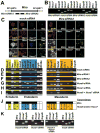
The epigenetic activator Mixed lineage leukemia 1 (MLL1) is paramount for embryonic development and hematopoiesis. Here, we demonstrate that the long, noncoding RNA (lncRNA) Mistral (Mira) activates transcription of the homeotic genes Hoxa6 and Hoxa7 in mouse embryonic stem cells (mESC) by recruiting MLL1 to chromatin. The Mira gene is located in the spacer DNA region (SDR) separating Hoxa6 and Hoxa7, transcriptionally silent in mESCs, and activated by retinoic acid. Mira-mediated recruitment of MLL1 to the Mira gene triggers dynamic changes in chromosome conformation, culminating in activation of Hoxa6 and Hoxa7 transcription. Hoxa6 and Hoxa7 activate the expression of genes involved in germ layer specification during mESC differentiation in a cooperative and redundant fashion. Our results connect the lncRNA Mira with the recruitment of MLL1 to target genes and implicate lncRNAs in epigenetic activation of gene expression during vertebrate cell-fate determination.
Copyright © 2011 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Figures

References
-
- Boyer LA, Plath K, Zeitlinger J, Brambrink T, Medeiro LA, Lee TI, Levine SS, Wernig M, Tajonar A, Ray MK, et al. Polycomb complexes repress developmental regulators in murine embryonic stem cells. Nature. 2006;441:349–353. - PubMed
-
- Carroll SB. Homeotic genes and the evolution of arthropods and chordates. Nature. 1995;376:479–485. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

