Anxiolytic effects of 5-HT₁A receptors and anxiogenic effects of 5-HT₂C receptors in the amygdala of mice
- PMID: 21925519
- PMCID: PMC3196065
- DOI: 10.1016/j.neuropharm.2011.09.002
Anxiolytic effects of 5-HT₁A receptors and anxiogenic effects of 5-HT₂C receptors in the amygdala of mice
Abstract
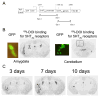
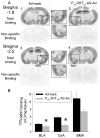
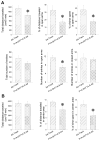
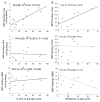
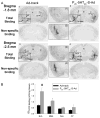
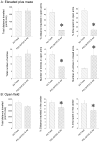
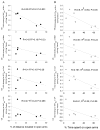
The aim of the present study is to test a hypothesis that 5-HT(1A) and 5-HT(2C) receptors in the amygdala play an important role in the regulation of anxiety behaviors. We examined alterations in anxiety-like behaviors after manipulation of the expression of 5-HT(1A) and 5-HT(2C) receptors in the amygdala using recombinant adenovirus approaches. Recombinant adenoviruses containing a 5-HT(1A) promoter-controlled 5-HT(1A) antisense sequence or a 5-HT(2C) promoter-controlled 5-HT(2C) sense sequence were injected into the amygdala. Elevated plus-maze (EPM) and open field tests were conducted to determine anxiety-like behavior and locomotor activity. Reductions in the expression of 5-HT(1A) receptors in the amygdala significantly attenuated the time spent in the open arms of EPM and time spent in the center of an open field. Reduction in the percent of time spent in the open arms of EPM is negatively correlated with the density of 5-HT(1A) receptors in the central amygdala. On the other hand, increased expression of 5-HT(2C) receptors reduced the time spent in the open arms of EPM and time spent in the center of an open field. The reductions in the time spent and distance traveled in the open arms of EPM were correlated to the density of 5-HT(2C) receptors in the basolateral nucleus of amygdala. These data suggest that amygdaloid 5-HT(1A) receptors produce anxiolytic and 5-HT(2C) receptors produce anxiogenic effects. Together, the present results demonstrate the important role of the amygdaloid 5-HT(1A) and 5-HT(2C) receptors in the regulation of anxiety-like behaviors. This article is part of a Special Issue entitled 'Anxiety and Depression'.
Copyright © 2011 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures
References
-
- Abe K, Fujimoto T, Akaishi T, Misawa M. Stimulation of basolateral amygdaloid serotonin 5-HT(2C) receptors promotes the induction of long-term potentiation in the dentate gyrus of anesthetized rats. Neurosci Lett. 2009;451:65–68. - PubMed
-
- Bagdy G, Graf M, Anheuer ZE, Modos EA, Kantor S. Anxiety-like effects induced by acute fluoxetine, sertraline or m-CPP treatment are reversed by pretreatment with the 5-HT2C receptor antagonist SB-242084 but not the 5-HT1A receptor antagonist WAY-100635. International Journal of Neuropsychopharmacology. 2001;4:399–408. - PubMed
-
- Campbell BM, Merchant KM. Serotonin 2C receptors within the basolateral amygdala induce acute fear-like responses in an open-field environment. Brain Research. 2003;993:1–9. - PubMed
-
- Cornelio AM, Nunes-De-Souza RL. Anxiogenic-like effects of mCPP microinfusions into the amygdala (but not dorsal or ventral hippocampus) in mice exposed to elevated plus-maze. Behavioural Brain Research. 2007;178:82–89. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

