Plastid signalling under multiple conditions is accompanied by a common defect in RNA editing in plastids
- PMID: 21926093
- PMCID: PMC3245456
- DOI: 10.1093/jxb/err257
Plastid signalling under multiple conditions is accompanied by a common defect in RNA editing in plastids
Abstract
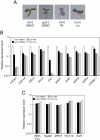
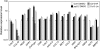
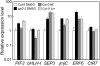
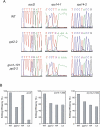
Retrograde signalling from the plastid to the nucleus, also known as plastid signalling, plays a key role in coordinating nuclear gene expression with the functional state of plastids. Inhibitors that cause plastid dysfunction have been suggested to generate specific plastid signals related to their modes of action. However, the molecules involved in plastid signalling remain to be identified. Genetic studies indicate that the plastid-localized pentatricopeptide repeat protein GUN1 mediates signalling under several plastid signalling-related conditions. To elucidate further the nature of plastid signals, investigations were carried out to determine whether different plastid signal-inducing treatments had similar effects on plastids and on nuclear gene expression. It is demonstrated that norflurazon and lincomycin treatments and the plastid protein import2-2 (ppi2-2) mutation, which causes a defect in plastid protein import, all resulted in similar changes at the gene expression level. Furthermore, it was observed that these three treatments resulted in defective RNA editing in plastids. This defect in RNA editing was not a secondary effect of down-regulation of pentatricopeptide repeat protein gene expression in the nucleus. The results indicate that these three treatments, which are known to induce plastid signals, affect RNA editing in plastids, suggesting an unprecedented link between plastid signalling and RNA editing.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The plastid transcription machinery and its coordination with the expression of nuclear genome: Plastid-Encoded Polymerase, Nuclear-Encoded Polymerase and the Genomes Uncoupled 1-mediated retrograde communication.Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 2020 Jun 22;375(1801):20190399. doi: 10.1098/rstb.2019.0399. Epub 2020 May 4. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 2020. PMID: 32362266 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Coordination of plastid protein import and nuclear gene expression by plastid-to-nucleus retrograde signaling.Plant Physiol. 2009 Nov;151(3):1339-53. doi: 10.1104/pp.109.145987. Epub 2009 Sep 2. Plant Physiol. 2009. PMID: 19726569 Free PMC article.
-
Sigma factor-mediated plastid retrograde signals control nuclear gene expression.Plant J. 2013 Jan;73(1):1-13. doi: 10.1111/tpj.12011. Epub 2012 Nov 5. Plant J. 2013. PMID: 22950756 Free PMC article.
-
The nuclear genes Lhcb and HEMA1 are differentially sensitive to plastid signals and suggest distinct roles for the GUN1 and GUN5 plastid-signalling pathways during de-etiolation.Plant J. 2004 Dec;40(5):672-85. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-313X.2004.02243.x. Plant J. 2004. PMID: 15546351
-
Influence of plastids on light signalling and development.Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 2014 Mar 3;369(1640):20130232. doi: 10.1098/rstb.2013.0232. Print 2014 Apr 19. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 2014. PMID: 24591718 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Induction of TOC and TIC genes during photomorphogenesis is mediated primarily by cryptochrome 1 in Arabidopsis.Sci Rep. 2020 Nov 20;10(1):20255. doi: 10.1038/s41598-020-76939-w. Sci Rep. 2020. PMID: 33219240 Free PMC article.
-
GENOMES UNCOUPLED PROTEIN1 binds to plastid RNAs and promotes their maturation.Plant Commun. 2024 Dec 9;5(12):101069. doi: 10.1016/j.xplc.2024.101069. Epub 2024 Aug 22. Plant Commun. 2024. PMID: 39169625 Free PMC article.
-
Plastids are major regulators of light signaling in Arabidopsis.Plant Physiol. 2012 May;159(1):366-90. doi: 10.1104/pp.112.193599. Epub 2012 Mar 1. Plant Physiol. 2012. PMID: 22383539 Free PMC article.
-
Salt stress affects mRNA editing in soybean chloroplasts.Genet Mol Biol. 2017;40(1 suppl 1):200-208. doi: 10.1590/1678-4685-GMB-2016-0055. Epub 2017 Mar 2. Genet Mol Biol. 2017. PMID: 28257523 Free PMC article.
-
The plastid transcription machinery and its coordination with the expression of nuclear genome: Plastid-Encoded Polymerase, Nuclear-Encoded Polymerase and the Genomes Uncoupled 1-mediated retrograde communication.Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 2020 Jun 22;375(1801):20190399. doi: 10.1098/rstb.2019.0399. Epub 2020 May 4. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 2020. PMID: 32362266 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Beck CF. Signaling pathways from the chloroplast to the nucleus. Planta. 2005;222:743–756. - PubMed
-
- Bradbeer JW, Atkinson YE, Börner T, Hagemann R. Cytoplasmic synthesis of plastid polypeptides may be controlled by plastid-synthesised RNA. Nature. 1979;279:816–817.
-
- Chamovitz D, Pecker I, Hirschberg J. The molecular basis of resistance to the herbicide norflurazon. Plant Molecular Biology. 1991;16:967–974. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

