Resistance to regulatory T cell-mediated suppression in rheumatoid arthritis can be bypassed by ectopic foxp3 expression in pathogenic synovial T cells
- PMID: 21926327
- PMCID: PMC3189031
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1112722108
Resistance to regulatory T cell-mediated suppression in rheumatoid arthritis can be bypassed by ectopic foxp3 expression in pathogenic synovial T cells
Abstract
Increasing evidence suggests that regulatory T cell (Treg) function is impaired in chronic inflammatory diseases such as rheumatoid arthritis (RA). Here we demonstrate that Tregs are unable to modulate the spontaneous production of TNF-α from RA synovial cells cultured from the diseased synovium site. Cytokine (IL-2, IL-6, TNF-α) activated T cells (Tck), cells we previously demonstrated to mimic the effector function of pathogenic RA synovial T cells, contained Tregs that survived and divided in this cytokine environment; however, the up-regulation of key molecules associated with Treg function (CTLA-4 and LFA-1) was impaired. Furthermore, Tregs were unable to suppress the function of Tcks, including contact-dependent induction of TNF-α from macrophages, supporting the concept that impaired Treg function/responsiveness contributes to chronicity of RA. However, ectopic foxp3 expression in both Tcks and pathogenic RA synovial T cells attenuated their cytokine production and function, including contact-dependent activation of macrophages. This diminished response to cytokine activation after ectopic foxp3 expression involved inhibited NF-κB activity and differed mechanistically from that displayed endogenously in conventional Tregs. These results suggest that diseases such as RA may perpetuate owing to the inability of Tregs to control cytokine-activated T-cell function. Understanding the mechanism whereby foxp3 attenuates the pathogenic function of synovial T cells may provide insight into the mechanisms of chronicity in inflammatory disease and potentially reveal new therapeutic candidates.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
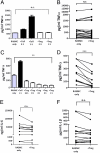
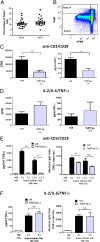
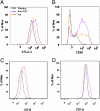
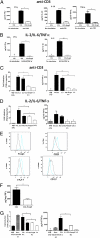
References
-
- Gregersen PK, Silver J, Winchester RJ. The shared epitope hypothesis. An approach to understanding the molecular genetics of susceptibility to rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 1987;30:1205–1213. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

