Mast cell chymase reduces the toxicity of Gila monster venom, scorpion venom, and vasoactive intestinal polypeptide in mice
- PMID: 21926462
- PMCID: PMC3195461
- DOI: 10.1172/JCI46139
Mast cell chymase reduces the toxicity of Gila monster venom, scorpion venom, and vasoactive intestinal polypeptide in mice
Abstract
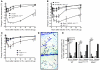
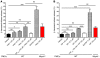
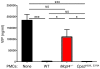
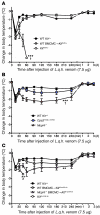
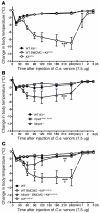
Mast cell degranulation is important in the pathogenesis of anaphylaxis and allergic disorders. Many animal venoms contain components that can induce mast cell degranulation, and this has been thought to contribute to the pathology and mortality caused by envenomation. However, we recently reported evidence that mast cells can enhance the resistance of mice to the venoms of certain snakes and that mouse mast cell-derived carboxypeptidase A3 (CPA3) can contribute to this effect. Here, we investigated whether mast cells can enhance resistance to the venom of the Gila monster, a toxic component of that venom (helodermin), and the structurally similar mammalian peptide, vasoactive intestinal polypeptide (VIP). Using 2 types of mast cell-deficient mice, as well as mice selectively lacking CPA3 activity or the chymase mouse mast cell protease-4 (MCPT4), we found that mast cells and MCPT4, which can degrade helodermin, can enhance host resistance to the toxicity of Gila monster venom. Mast cells and MCPT4 also can limit the toxicity associated with high concentrations of VIP and can reduce the morbidity and mortality induced by venoms from 2 species of scorpions. Our findings support the notion that mast cells can enhance innate defense by degradation of diverse animal toxins and that release of MCPT4, in addition to CPA3, can contribute to this mast cell function.
Figures
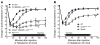
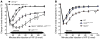

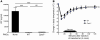
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

