BAX inhibitor-1 regulates autophagy by controlling the IRE1α branch of the unfolded protein response
- PMID: 21926971
- PMCID: PMC3230375
- DOI: 10.1038/emboj.2011.318
BAX inhibitor-1 regulates autophagy by controlling the IRE1α branch of the unfolded protein response
Erratum in
-
BAX inhibitor-1 regulates autophagy by controlling the IRE1α branch of the unfolded protein response.EMBO J. 2017 Jun 1;36(11):1640. doi: 10.15252/embj.201797020. EMBO J. 2017. PMID: 28572284 Free PMC article.
-
BAX inhibitor-1 regulates autophagy by controlling the IRE1α branch of the unfolded protein response.EMBO J. 2021 Nov 2;40(21):e109149. doi: 10.15252/embj.2021109149. EMBO J. 2021. PMID: 34726286 Free PMC article.
Abstract
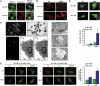
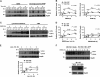
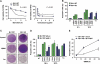
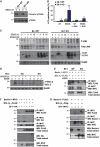
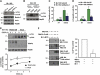
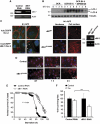
Both autophagy and apoptosis are tightly regulated processes playing a central role in tissue homeostasis. Bax inhibitor 1 (BI-1) is a highly conserved protein with a dual role in apoptosis and endoplasmic reticulum (ER) stress signalling through the regulation of the ER stress sensor inositol requiring kinase 1 α (IRE1α). Here, we describe a novel function of BI-1 in the modulation of autophagy. BI-1-deficient cells presented a faster and stronger induction of autophagy, increasing LC3 flux and autophagosome formation. These effects were associated with enhanced cell survival under nutrient deprivation. Repression of autophagy by BI-1 was dependent on cJun-N terminal kinase (JNK) and IRE1α expression, possibly due to a displacement of TNF-receptor associated factor-2 (TRAF2) from IRE1α. Targeting BI-1 expression in flies altered autophagy fluxes and salivary gland degradation. BI-1 deficiency increased flies survival under fasting conditions. Increased expression of autophagy indicators was observed in the liver and kidney of bi-1-deficient mice. In summary, we identify a novel function of BI-1 in multicellular organisms, and suggest a critical role of BI-1 as a stress integrator that modulates autophagy levels and other interconnected homeostatic processes.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures
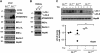
References
-
- Ahn T, Yun CH, Kim HR, Chae HJ (2010) Cardiolipin, phosphatidylserine, and BH4 domain of Bcl-2 family regulate Ca2+/H+ antiporter activity of human Bax inhibitor-1. Cell Calcium 47: 387–396 - PubMed
-
- Bailly-Maitre B, Belgardt BF, Jordan SD, Coornaert B, von Freyend MJ, Kleinridders A, Mauer J, Cuddy M, Kress CL, Willmes D, Essig M, Hampel B, Protzer U, Reed JC, Bruning JC (2010) Hepatic Bax inhibitor-1 inhibits IRE1alpha and protects from obesity-associated insulin resistance and glucose intolerance. J Biol Chem 285: 6198–6207 - PMC - PubMed
-
- Bailly-Maitre B, Fondevila C, Kaldas F, Droin N, Luciano F, Ricci JE, Croxton R, Krajewska M, Zapata JM, Kupiec-Weglinski JW, Farmer D, Reed JC (2006) Cytoprotective gene bi-1 is required for intrinsic protection from endoplasmic reticulum stress and ischemia-reperfusion injury. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 103: 2809–2814 - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

