A Staphylococcus aureus pore-forming toxin subverts the activity of ADAM10 to cause lethal infection in mice
- PMID: 21926978
- PMCID: PMC3192248
- DOI: 10.1038/nm.2451
A Staphylococcus aureus pore-forming toxin subverts the activity of ADAM10 to cause lethal infection in mice
Abstract
Staphylococcus aureus is a major cause of human disease, responsible for half a million infections and approximately 20,000 deaths per year in the United States alone. This pathogen secretes α-hemolysin, a pore-forming cytotoxin that contributes to the pathogenesis of pneumonia. α-hemolysin injures epithelial cells in vitro by interacting with its receptor, the zinc-dependent metalloprotease ADAM10 (ref. 6). We show here that mice harboring a conditional disruption of the Adam10 gene in lung epithelium are resistant to lethal pneumonia. Investigation of the molecular mechanism of toxin-receptor function revealed that α-hemolysin upregulates ADAM10 metalloprotease activity in alveolar epithelial cells, resulting in cleavage of the adherens junction protein E-cadherin. Cleavage is associated with disruption of epithelial barrier function, contributing to the pathogenesis of lethal acute lung injury. A metalloprotease inhibitor of ADAM10 prevents E-cadherin cleavage in response to Hla; similarly, toxin-dependent E-cadherin proteolysis and barrier disruption is attenuated in ADAM10-knockout mice. Together, these data attest to the function of ADAM10 as the cellular receptor for α-hemolysin. The observation that α-hemolysin can usurp the metalloprotease activity of its receptor reveals a previously unknown mechanism of pore-forming cytotoxin action in which pathologic insults are not solely the result of irreversible membrane injury and defines ADAM10 inhibition as a strategy to attenuate α-hemolysin-induced disease.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
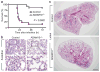
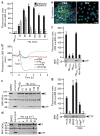
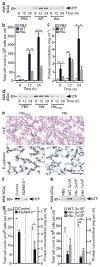
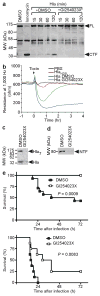
Comment in
-
Bacterial toxins: breaking the barrier.Nat Rev Microbiol. 2011 Oct 3;9(11):768. doi: 10.1038/nrmicro2672. Nat Rev Microbiol. 2011. PMID: 21963802 No abstract available.
References
-
- Klevens RM, et al. Invasive methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus infections in the United States. Jama. 2007;298:1763–1771. - PubMed
-
- Otto M. Basis of virulence in community-associated methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus. Annu Rev Microbiol. 2010;64:143–162. - PubMed
-
- Bubeck Wardenburg J, Bae T, Otto M, Deleo FR, Schneewind O. Poring over pores: alpha-hemolysin and Panton-Valentine leukocidin in Staphylococcus aureus pneumonia. Nat Med. 2007;13:1405–1406. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

