Novel gastroretentive sustained-release tablet of tacrolimus based on self-microemulsifying mixture: in vitro evaluation and in vivo bioavailability test
- PMID: 21927013
- PMCID: PMC4010087
- DOI: 10.1038/aps.2011.90
Novel gastroretentive sustained-release tablet of tacrolimus based on self-microemulsifying mixture: in vitro evaluation and in vivo bioavailability test
Abstract
Aim: To develop a novel gastroretentive drug delivery system based on a self-microemulsifying (SME) lipid mixture for improving the oral absorption of the immunosuppressant tacrolimus.
Methods: Liquid SME mixture, composed of Cremophor RH40 and monocaprylin glycerate, was blended with polyethylene oxide, chitosan, polyvinylpyrrolidone and mannitol, and then transformed into tablets via granulation, with ethanol as the wetting agent. The tablets were characterized in respect of swelling, bioadhesive and SME properties. In vitro dissolution was conducted using an HCl buffer at pH 1.2. Oral bioavailability of the tablets was examined in fasted beagle dogs.
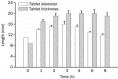
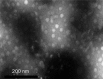
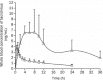
Results: The tablet could expand to 13.5 mm in diameter and 15 mm in thickness during the initial 20 min of contact with the HCl buffer at pH 1.2. The bioadhesive strength was as high as 0.98±0.06 N/cm(2). The SME gastroretentive sustained-release tablets preserved the SME capability of the liquid SME formations under transmission electron microscope. The drug-release curve was fit to the zero-order release model, which was helpful in reducing fluctuations in blood concentration. Compared with the commercially available capsules of tacrolimus, the relative bioavailability of the SME gastroretentive sustained-release tablets was 553.4%±353.8%.
Conclusion: SME gastroretentive sustained-release tablets can enhance the oral bioavailability of tacrolimus with poor solubility and a narrow absorption window.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Enhanced oral bioavailability of felodipine by novel solid self-microemulsifying tablets.Drug Dev Ind Pharm. 2016;42(3):506-12. doi: 10.3109/03639045.2015.1058816. Epub 2015 Jul 15. Drug Dev Ind Pharm. 2016. PMID: 26177197
-
Development of Solidified Self-microemulsifying Delivery Systems Containing Tacrolimus for Enhanced Dissolution and Pharmacokinetic Profile.AAPS J. 2024 Nov 22;27(1):6. doi: 10.1208/s12248-024-00992-w. AAPS J. 2024. PMID: 39572417
-
Enhanced oral bioavailability of tacrolimus in rats by self-microemulsifying drug delivery systems.Drug Dev Ind Pharm. 2011 Oct;37(10):1225-30. doi: 10.3109/03639045.2011.565774. Epub 2011 May 26. Drug Dev Ind Pharm. 2011. PMID: 21615281
-
Clinical Pharmacokinetics of Once-Daily Tacrolimus in Solid-Organ Transplant Patients.Clin Pharmacokinet. 2015 Oct;54(10):993-1025. doi: 10.1007/s40262-015-0282-2. Clin Pharmacokinet. 2015. PMID: 26038096 Review.
-
Advanced polymers and recent advancements on gastroretentive drug delivery system; a comprehensive review.J Drug Target. 2024 Jul;32(6):655-671. doi: 10.1080/1061186X.2024.2347366. Epub 2024 Apr 29. J Drug Target. 2024. PMID: 38652465 Review.
Cited by
-
Features and Facts of a Gastroretentive Drug Delivery System-A Review.Turk J Pharm Sci. 2022 Aug 31;19(4):476-487. doi: 10.4274/tjps.galenos.2021.44959. Turk J Pharm Sci. 2022. PMID: 36047602 Free PMC article.
-
Automatic Dissolution Testing with High-Temporal Resolution for Both Immediate-Release and Fixed-Combination Drug Tablets.Sci Rep. 2019 Nov 19;9(1):17114. doi: 10.1038/s41598-019-53750-w. Sci Rep. 2019. PMID: 31745201 Free PMC article.
-
Current Status of Supersaturable Self-Emulsifying Drug Delivery Systems.Pharmaceutics. 2020 Apr 16;12(4):365. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics12040365. Pharmaceutics. 2020. PMID: 32316199 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Chitosan Coated Textiles May Improve Atopic Dermatitis Severity by Modulating Skin Staphylococcal Profile: A Randomized Controlled Trial.PLoS One. 2015 Nov 30;10(11):e0142844. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0142844. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 26618557 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
In Vitro and In Vivo Test Methods for the Evaluation of Gastroretentive Dosage Forms.Pharmaceutics. 2019 Aug 16;11(8):416. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics11080416. Pharmaceutics. 2019. PMID: 31426417 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Yamashita K, Nakate T, Okimoto K, Ohike A, Tokunaga Y, Ibuki R, et al. Establishment of new preparation method for solid dispersion formulation of tacrolimus. Int J Pharm. 2003;267:79–91. - PubMed
-
- Kino T, Hatanaka H, Hashimoto M, Nishiyama M, Goto T, Okuhara M, et al. FK 506, a novel immunosuppressant isolated from a Streptomyces I. Fermentation, isolation and physico-chemical and biological characteristics. J Antibiot. 1987;42:1249–55. - PubMed
-
- Plosker GL, Foster RH. Tacrolimus-a further update of its pharmacology and therapeutic use in the management of organ transplantation. Drugs. 2000;59:323–89. - PubMed
-
- Abdalla A, Klein S, Mader K. A new self-emulsifying drug delivery system (SEDDS) for poorly soluble drugs: characterization, dissolution, in vitro digestion and incorporation into solid pellets. Eur J Pharm Sci. 2008;35:457–64. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

