Spo11 and the Formation of DNA Double-Strand Breaks in Meiosis
- PMID: 21927624
- PMCID: PMC3172816
- DOI: 10.1007/7050_2007_026
Spo11 and the Formation of DNA Double-Strand Breaks in Meiosis
Abstract
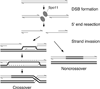
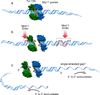
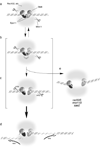
Meiotic recombination is carried out through a specialized pathway for the formation and repair of DNA double-strand breaks made by the Spo11 protein, a relative of archaeal topoisomerase VI. This review summarizes recent studies that provide insight to the mechanism of DNA cleavage by Spo11, functional interactions of Spo11 with other proteins required for break formation, mechanisms that control the timing of recombination initiation, and evolutionary conservation and divergence of these processes.
Figures



References
-
- Agashe B, Prasad CK, Siddiqi I. Identification and analysis of DYAD: a gene required for meiotic chromosome organisation and female meiotic progression in Arabidopsis. Development. 2002;129:3935–3943. - PubMed
-
- Alani E, Padmore R, Kleckner N. Analysis of wild-type and rad50 mutants of yeast suggests an intimate relationship between meiotic chromosome synapsis and recombination. Cell. 1990;61:419–436. - PubMed
-
- Arora C, Kee K, Maleki S, Keeney S. Antiviral protein Ski8 is a direct partner of Spo11 in meiotic DNA break formation, independent of its cytoplasmic role in RNA metabolism. Mol Cell. 2004;13:549–559. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
