A Three-Channel Spectrometer for Wide-Field Imaging of Anisotropic Plasmonic Nanoparticles
- PMID: 21927639
- PMCID: PMC3171732
- DOI: 10.1021/jp206157v
A Three-Channel Spectrometer for Wide-Field Imaging of Anisotropic Plasmonic Nanoparticles
Abstract
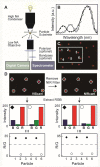
A three-channel spectrometer (3CS) based on a commercial digital camera was developed to distinguish among tens of large (>100 nm), anisotropic plasmonic particles with various shapes, orientations, and compositions on a surface simultaneously. Using band pass filters and polarizers, the contrast of 3CS images could be enhanced to identify specific orientation and composition characteristics of gold and gold-silver nanopyramids and as well as the direction of the longest arm of gold nanostars.
Figures
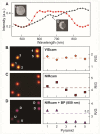
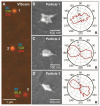
 ) and tip-down (D) (▲) orientation. (B) VIScam image and R/G values for five Au pyramids. The particles scatter very similar colors and have very similar R/G values. (C) NIRcam image and R/G values for the same image in (B). The particles still scatter very similar colors, although the R/G values for pyramids 1 and 2 begin to separate from pyramids 3, 4, 5. (D) NIRcam image with 850 nm (± 20 nm) BP filter and R/G values for the same image in (B). The R/G values separate into two distinct regions that correspond to U and D. The threshold value was set at 3.2. All optical images are 12 μm × 9.3 μm.
) and tip-down (D) (▲) orientation. (B) VIScam image and R/G values for five Au pyramids. The particles scatter very similar colors and have very similar R/G values. (C) NIRcam image and R/G values for the same image in (B). The particles still scatter very similar colors, although the R/G values for pyramids 1 and 2 begin to separate from pyramids 3, 4, 5. (D) NIRcam image with 850 nm (± 20 nm) BP filter and R/G values for the same image in (B). The R/G values separate into two distinct regions that correspond to U and D. The threshold value was set at 3.2. All optical images are 12 μm × 9.3 μm.

References
-
- Stephens DJ, Allan VJ. Science. 2003;300:82. - PubMed
-
- Penn SG, He L, Natan MJ. Curr. Opin. Chem. Biol. 2003;7:609. - PubMed
-
- Bohren C, Huffman DR, editors. Absorption and Scattering of Light by Small Particles. Wiley-VCH; New York: 1999.
-
- Jain P, Huang X, El-Sayed I, El-Sayed M. Plasmonics. 2007;2:107.
-
- Jain PK, Lee KS, El-Sayed IH, El-Sayed MA. J. Phys. Chem. B. 2006;110:7238. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
