(3-Cyano-5-fluorophenyl)biaryl negative allosteric modulators of mGlu(5): Discovery of a new tool compound with activity in the OSS mouse model of addiction
- PMID: 21927650
- PMCID: PMC3172161
- DOI: 10.1021/cn100099n
(3-Cyano-5-fluorophenyl)biaryl negative allosteric modulators of mGlu(5): Discovery of a new tool compound with activity in the OSS mouse model of addiction
Abstract
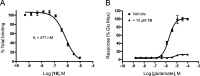
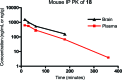
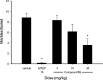
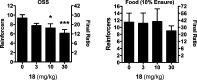
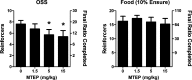
Glutamate is the major excitatory transmitter in the mammalian CNS, exerting its effects through both ionotropic and metabotropic glutamate receptors. The metabotropic glutamate receptors (mGlus) belong to family C of the G-protein-coupled receptors (GPCRs). The eight mGlus identified to date are classified into three groups based on their structure, preferred signal transduction mechanisms, and pharmacology (Group I: mGlu(1) and mGlu(5); Group II: mGlu(2) and mGlu(3); Group III: mGlu(4), mGlu(6), mGlu(7), and mGlu(8)). Non-competitive antagonists, also known as negative allosteric modulators (NAMs), of mGlu(5) offer potential therapeutic applications in diseases such as pain, anxiety, gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD), Parkinson's disease (PD), fragile X syndrome, and addiction. The development of SAR in a (3-cyano-5-fluorophenyl)biaryl series using our functional cell-based assay is described in this communication. Further characterization of a selected compound, 3-fluoro-5-(2-methylbenzo[d]thiazol-5-yl)benzonitrile, in additional cell based assays as well as in vitro assays designed to measure its metabolic stability and protein binding indicated its potential utility as an in vivo tool. Subsequent evaluation of the same compound in a pharmacokinetic study using intraperitoneal dosing in mice showed good exposure in both plasma and brain samples. The compound was efficacious in a mouse marble burying model of anxiety, an assay known to be sensitive to mGlu(5) antagonists. A new operant model of addiction termed operant sensation seeking (OSS) was chosen as a second behavioral assay. The compound also proved efficacious in the OSS model and constitutes the first reported example of efficacy with a small molecule mGlu(5) NAM in this novel assay.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Development of allosteric modulators of GPCRs for treatment of CNS disorders.Neurobiol Dis. 2014 Jan;61:55-71. doi: 10.1016/j.nbd.2013.09.013. Epub 2013 Sep 27. Neurobiol Dis. 2014. PMID: 24076101 Free PMC article. Review.
-
3-Cyano-5-fluoro-N-arylbenzamides as negative allosteric modulators of mGlu(5): Identification of easily prepared tool compounds with CNS exposure in rats.Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2010 Aug 1;20(15):4390-4. doi: 10.1016/j.bmcl.2010.06.064. Epub 2010 Jun 15. Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2010. PMID: 20598884 Free PMC article.
-
Allosteric modulation of metabotropic glutamate receptors.Adv Pharmacol. 2011;62:37-77. doi: 10.1016/B978-0-12-385952-5.00010-5. Adv Pharmacol. 2011. PMID: 21907906 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Pharmacology of metabotropic glutamate receptor allosteric modulators: structural basis and therapeutic potential for CNS disorders.Prog Mol Biol Transl Sci. 2013;115:61-121. doi: 10.1016/B978-0-12-394587-7.00002-6. Prog Mol Biol Transl Sci. 2013. PMID: 23415092 Review.
-
Recent advances in the design and development of novel negative allosteric modulators of mGlu(5).ACS Chem Neurosci. 2011 Aug 17;2(8):411-432. doi: 10.1021/cn2000266. ACS Chem Neurosci. 2011. PMID: 21927649 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Cannabinoid Receptor 1 and Fatty Acid Amide Hydrolase Contribute to Operant Sensation Seeking in Mice.Int J Mol Sci. 2017 Jul 27;18(8):1635. doi: 10.3390/ijms18081635. Int J Mol Sci. 2017. PMID: 28749428 Free PMC article.
-
Discovery of 2-(2-benzoxazoyl amino)-4-aryl-5-cyanopyrimidine as negative allosteric modulators (NAMs) of metabotropic glutamate receptor 5 (mGlu₅): from an artificial neural network virtual screen to an in vivo tool compound.ChemMedChem. 2012 Mar 5;7(3):406-14. doi: 10.1002/cmdc.201100510. Epub 2012 Jan 20. ChemMedChem. 2012. PMID: 22267125 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Identification of Nitazoxanide as a Group I Metabotropic Glutamate Receptor Negative Modulator for the Treatment of Neuropathic Pain: An In Silico Drug Repositioning Study.Pharm Res. 2015 Aug;32(8):2798-807. doi: 10.1007/s11095-015-1665-7. Epub 2015 Mar 12. Pharm Res. 2015. PMID: 25762088
-
Discovery of VU0409106: A negative allosteric modulator of mGlu5 with activity in a mouse model of anxiety.Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2013 Nov 1;23(21):5779-85. doi: 10.1016/j.bmcl.2013.09.001. Epub 2013 Sep 10. Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2013. PMID: 24074843 Free PMC article.
-
Substituted 1-Phenyl-3-(pyridin-2-yl)urea negative allosteric modulators of mGlu5: discovery of a new tool compound VU0463841 with activity in rat models of cocaine addiction.ACS Chem Neurosci. 2013 Aug 21;4(8):1217-28. doi: 10.1021/cn400070k. Epub 2013 May 29. ACS Chem Neurosci. 2013. PMID: 23682684 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Schoepp D. D.; Jane D. E.; Monn J. A. (1999) Pharmacological agents acting at subtypes of metabotropic glutamate receptors. Neuropharmacology 38, 1431–1476. - PubMed
-
- Conn P. J.; Pin J.-P. (1997) Pharmacology and functions of metabotropic glutamate receptors. Annu. Rev. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 37, 205–237. - PubMed
-
- Ritzén A.; Mathiesen J. M.; Thomsen C. (2005) Molecular pharmacology and therapeutic prospects of metabotropic glutamate receptor allosteric modulators. Basic Clin. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 97, 202–213. - PubMed
-
- Kew J. N. C. (2004) Positive and negative allosteric modulation of metabotropic glutamate receptors: emerging therapeutic potential. Pharmacol. Ther. 104, 233–244. - PubMed
-
- Lindsley C. W.; Emmitte K. A. (2009) Recent progress in the discovery and development of negative allosteric modulators of mGluR5. Curr. Opin. Drug Discovery Dev. 12, 446–457. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

