CD40/CD40 ligand interactions in immune responses and pulmonary immunity
- PMID: 21928689
- PMCID: PMC4831216
CD40/CD40 ligand interactions in immune responses and pulmonary immunity
Abstract
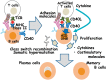
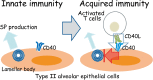
The CD40 ligand/CD40 pathway is widely recognized for its prominent role in immune regulation and homeostasis. CD40, a member of the tumor necrosis factor receptor family, is expressed by antigen-presenting cells, as well as non-immune cells and tumors. The engagement of the CD40 and CD40 ligands, which are transiently expressed on T cells and other non-immune cells under inflammatory conditions, regulates a wide spectrum of molecular and cellular processes, including the initiation and progression of cellular and humoral adaptive immunity. Based on recent research findings, the engagement of the CD40 with a deregulated amount of CD40 ligand has been implicated in a number of inflammatory diseases. We will discuss the involvement of the CD40 ligand/CD40 interaction in the pathophysiology of inflammatory diseases, including autoimmune diseases, atherothrombosis, cancer, and respiratory diseases.
Figures

Comment in
-
The fruits of CD40 research in basic and clinical medicine will soon be harvested.Nagoya J Med Sci. 2023 Feb;85(1):21-22. doi: 10.18999/nagjms.85.1.21. Nagoya J Med Sci. 2023. PMID: 36923637 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Germain RN, Stefanova I. The dynamics of T cell receptor signaling: complex orchestration and the key roles of tempo and cooperation. Annu Rev Immunol, 1999; 17: 467–522. - PubMed
-
- Croft M. Co-stimulatory members of the TNFR family: keys to effective T-cell immunity? Nat Rev Immunol, 2003; 3: 609–620. - PubMed
-
- Grewal IS, Flavell RA. CD40 and CD154 in cell-mediated immunity. Annu Rev Immunol, 1998; 16: 111–135. - PubMed
-
- van Kooten C, Banchereau J. CD40-CD40 ligand. J Leukoc Biol, 2000; 67: 2–17. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
