Preoperative regional cerebral oxygen saturation is a predictor of postoperative delirium in on-pump cardiac surgery patients: a prospective observational trial
- PMID: 21929765
- PMCID: PMC3334763
- DOI: 10.1186/cc10454
Preoperative regional cerebral oxygen saturation is a predictor of postoperative delirium in on-pump cardiac surgery patients: a prospective observational trial
Abstract
Introduction: Postoperative delirium is an important problem in patients undergoing major surgery. Cerebral oximetry is a non-invasive method to detect imbalances in the cerebral oxygen supply/demand-ratio. Low preoperative cerebral oxygen saturation (ScO₂) levels have been associated with postoperative delirium in non-cardiac surgery patients. The present prospective observational study determines the relationship between pre- and intra-operative ScO₂ levels and postoperative delirium in patients undergoing on-pump cardiac surgery.
Methods: After approval of the local ethical committee and written informed consent, N = 231 patients scheduled for elective/urgent cardiac surgery were enrolled. Delirium was assessed by the confusion-assessment-method for the intensive care unit (CAM-ICU) on the first three days after surgery. ScO₂ was obtained on the day before surgery, immediately before surgery and throughout the surgical procedure. Preoperative cognitive function, demographic, surgery related, and intra- and post-operative physiological data were registered.
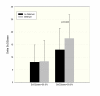
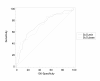
Results: Patients with delirium had lower pre- and intra-operative ScO₂ readings, were older, had lower mini-mental-status-examination(MMSE) scores, higher additive EuroScore and lower preoperative haemoglobin-levels. The binary logistic regression identified older age, lower MMSE, neurological or psychiatric disease and lower preoperative ScO₂ as independent predictors of postoperative delirium.
Conclusions: The presented study shows that a low preoperative ScO₂ is associated with postoperative delirium after on-pump cardiac surgery.
Figures

References
-
- Chang Y-L, Tsai Y-F, Lin P-J, Chen M-C, Liu C-Y. Prevalence and risk factors for postoperative delirium in a cardiovascular intensive care unit. Am J Crit Care. 2008;17:567–575. - PubMed
-
- Rudolph JL, Jones RN, Levkoff SE, Rockett C, Inouye SK, Sellke FW, Khuri SF, Lipsitz LA, Ramlawi B, Levitsky S, Marcantonio ER. Derivation and validation of a preoperative prediction rule for delirium after cardiac surgery. Circulation. 2009;119:229–236. doi: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.108.795260. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

