The management of oesophageal soft food bolus obstruction: a systematic review
- PMID: 21929913
- PMCID: PMC3369328
- DOI: 10.1308/003588411X588090
The management of oesophageal soft food bolus obstruction: a systematic review
Abstract
Introduction: Oesophageal soft food bolus obstruction (OSFBO) is a surgical emergency. However, no national guidelines exist regarding its management. This paper systematically reviews the literature with respect to the management of OSFBO.
Methods: Relevant studies included were identified from the the Cochrane Library, the National Center for Biotechnology Information and the US National Library of Medicine resources. A systematic review was performed on 8 November 2010.
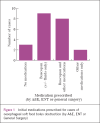
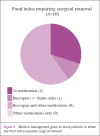
Results: This systematic review of the management of OSFBO shows no evidence that any medical intervention is more effective than a 'watch and wait' policy in enabling spontaneous disimpaction. Furthermore, the use of hyoscine butylbromide for OSFBO probably stems from a misquoted textbook. Surgical removal of an OSFBO is effective but not without potential risk. There is some evidence to support surgical intervention within 24 hours to prevent complications deriving from the initial obstruction.
Conclusions: There is a need for large double-blind, randomised, placebo controlled trials of drugs used in the medical management of OSFBO. Until the results from such trials are available, the treatment of OSFBO will remain based on inconsistent clinical judgement.
Figures

References
-
- Smith MT, Wong RK. Foreign bodies. Gastrointest Endosc Clin N Am. 2007;17:361–382. - PubMed
-
- Weissberg D, Refaely Y. Foreign bodies in the esophagus. Ann Thorac Surg. 2007;84:1,854–1,857. - PubMed
-
- Thomas L, Webb C, Duvvi S, et al. Is buscopan effective in meat bolus obstruction? Clin Otolaryngol. 2005;30:183–185. - PubMed
-
- Basavaraj S, Penumetcha KR, Cable HR, Umapathy N. Buscopan in oesophageal food bolus: is it really effective? Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol. 2005;262:524–527. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

