Localization of sclerotic-type chronic graft-vs-host disease to sites of skin injury: potential insight into the mechanism of isomorphic and isotopic responses
- PMID: 21931046
- PMCID: PMC7384357
- DOI: 10.1001/archdermatol.2011.226
Localization of sclerotic-type chronic graft-vs-host disease to sites of skin injury: potential insight into the mechanism of isomorphic and isotopic responses
Abstract
Background: The mechanisms responsible for the variable manifestations of chronic cutaneous graft-vs-host disease (cGVHD) are poorly understood. Localization of sclerotic-type chronic graft-vs-host disease to sites of skin injury (isomorphic and isotopic responses), a recognized phenomenon in morphea, suggests a potential common pathway between cGVHD and other sclerotic skin conditions.
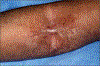
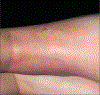
Observations: Four cases of sclerotic-type cGVHD developed at the site of disparate skin injuries (ionizing radiotherapy, repeated needle sticks, central catheter site, and varicella-zoster virus infection). We review the spectrum of previously reported cases of sclerotic and nonsclerotic cGVHD relating to external forces on the skin.
Conclusions: Localization of sclerotic-type cGVHD may occur after many types of skin injury, including UV and ionizing radiotherapy, needle sticks, viral infection, and pressure or friction. Recognition of this phenomenon may be helpful for the early diagnosis of sclerotic disease. Recent insights into the immunological consequences of minor skin injury may provide important clues to the underlying pathogenesis of cGVHD-mediated skin disease.
Figures


References
-
- Filipovich AH. Diagnosis and manifestations of chronic graft-versus-host disease. Best Pract Res Clin Haematol. 2008;21(2):251–257. - PubMed
-
- Ehara M, Oono T, Yamasaki O, Matsuura H, Iwatsuki K. Generalized morphealike lesions arising in mechanically-compressed areas by underclothes. Eur J Dermatol. 2006;16(3):307–309. - PubMed
-
- Rubin AI, Stiller MJ. A listing of skin conditions exhibiting the Koebner and pseudo-Koebner phenomena with eliciting stimuli. J Cutan Med Surg. 2002;6(1):29–34. - PubMed
-
- Baselga E, Drolet BA, Segura AD, Leonardi CL, Esterly NB. Dermatomal lichenoid chronic graft-vs-host disease following varicella-zoster infection despite absence of viral genome. J Cutan Pathol. 1996;23(6):576–581. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

