Adhesion of osteoblasts to a nanorough titanium implant surface
- PMID: 21931478
- PMCID: PMC3173045
- DOI: 10.2147/IJN.S21755
Adhesion of osteoblasts to a nanorough titanium implant surface
Abstract
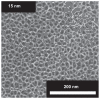
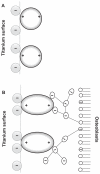
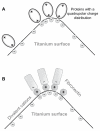
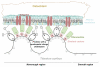
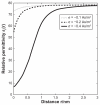
This work considers the adhesion of cells to a nanorough titanium implant surface with sharp edges. The basic assumption was that the attraction between the negatively charged titanium surface and a negatively charged osteoblast is mediated by charged proteins with a distinctive quadrupolar internal charge distribution. Similarly, cation-mediated attraction between fibronectin molecules and the titanium surface is expected to be more efficient for a high surface charge density, resulting in facilitated integrin mediated osteoblast adhesion. We suggest that osteoblasts are most strongly bound along the sharp convex edges or spikes of nanorough titanium surfaces where the magnitude of the negative surface charge density is the highest. It is therefore plausible that nanorough regions of titanium surfaces with sharp edges and spikes promote the adhesion of osteoblasts.
Keywords: adhesion; nanostructures; osteoblasts; osteointegration; titanium implants.
Figures
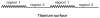


Similar articles
-
Mechanics and electrostatics of the interactions between osteoblasts and titanium surface.Comput Methods Biomech Biomed Engin. 2011 May;14(5):469-82. doi: 10.1080/10255842.2010.534986. Comput Methods Biomech Biomed Engin. 2011. PMID: 21516531
-
Adhesion of osteoblasts to a vertically aligned TiO2 nanotube surface.Mini Rev Med Chem. 2013 Feb;13(2):194-200. Mini Rev Med Chem. 2013. PMID: 22931535 Review.
-
Superposition of nanostructures on microrough titanium-aluminum-vanadium alloy surfaces results in an altered integrin expression profile in osteoblasts.Connect Tissue Res. 2014 Aug;55 Suppl 1(0 1):164-8. doi: 10.3109/03008207.2014.923881. Connect Tissue Res. 2014. PMID: 25158204 Free PMC article.
-
Greater osteoblast and endothelial cell adhesion on nanostructured polyethylene and titanium.Int J Nanomedicine. 2010 Sep 7;5:647-52. doi: 10.2147/IJN.S13047. Int J Nanomedicine. 2010. PMID: 20856840 Free PMC article.
-
Balancing osteoblast functions and bacterial adhesion on functionalized titanium surfaces.Biomaterials. 2012 Apr;33(10):2813-22. doi: 10.1016/j.biomaterials.2012.01.018. Epub 2012 Jan 16. Biomaterials. 2012. PMID: 22257725 Review.
Cited by
-
Design, Synthesis, and Preliminary Evaluation for Ti-Mo-Zr-Ta-Si Alloys for Potential Implant Applications.Materials (Basel). 2021 Nov 11;14(22):6806. doi: 10.3390/ma14226806. Materials (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34832207 Free PMC article.
-
Generalized stern models of the electric double layer considering the spatial variation of permittvity and finite size of ions in saturation regime.Cell Mol Biol Lett. 2011 Dec;16(4):576-94. doi: 10.2478/s11658-011-0024-x. Epub 2011 Aug 16. Cell Mol Biol Lett. 2011. PMID: 21847663 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Effects of Cold Atmospheric Plasma Pre-Treatment of Titanium on the Biological Activity of Primary Human Gingival Fibroblasts.Biomedicines. 2023 Apr 16;11(4):1185. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines11041185. Biomedicines. 2023. PMID: 37189803 Free PMC article.
-
Atomic Layer Deposition of ZrO2 on Titanium Inhibits Bacterial Adhesion and Enhances Osteoblast Viability.Int J Nanomedicine. 2021 Feb 24;16:1509-1523. doi: 10.2147/IJN.S298449. eCollection 2021. Int J Nanomedicine. 2021. PMID: 33658781 Free PMC article.
-
Different diameters of titanium dioxide nanotubes modulate Saos-2 osteoblast-like cell adhesion and osteogenic differentiation and nanomechanical properties of the surface.RSC Adv. 2019 Apr 11;9(20):11341-11355. doi: 10.1039/c9ra00761j. eCollection 2019 Apr 9. RSC Adv. 2019. PMID: 35520235 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Lüthen F, Lange R, Becker P, Rychly J, Beck U, Nebe B. The influence of surface roughness of titanium on 1-βand 3-βintegrin adhesion and the organization of fibronectin in human osteoblastic cells. Biomaterials. 2004;26:2423–2440. - PubMed
-
- Nebe B, Lüthen F, Lange R, Beck U. Interface interactions of osteoblasts with structured titanium and the correlation between physicochemical characteristics and cell biological parameters. Macromol Biosci. 2007;7:567–578. - PubMed
-
- Anselme K. Osteoblast adhesion on biomaterials. Biomaterials. 2000;21:667–681. - PubMed
-
- Anselme K, Bigerelle M, Noel B, et al. Qualitative and quantitative study of human osteoblast adhesion on materials with various surface roughness. J Biomed Mater Res. 2000;49:155–166. - PubMed
-
- Shelton RM, Rasmussen AC, Davies JE. Protein adsorption at the interface between charged polymer substrata and migrating osteoblasts. Biomaterials. 1998;9:24–29. - PubMed
Appendix references
-
- Lamperski S, Outhwaite CW. Volume term in the inhomogeneous Poisson-Boltzmann theory for high surface charge. Langmuir. 2002;18:3423–3424.
-
- Iglič A, Gongadze E, Bohinc K. Excluded volume effect and orientational ordering near charged surface in solution of ions and Langevin dipoles. Bioelectrochemistry. 2010;79:223–227. - PubMed
-
- Gongadze E, Bohinc K, van Rienen U, Kralj-Iglič V, Iglič A. Spatial variation of permittivity near a charged membrane in contact with electrolyte solution. In: Iglič A, editor. Advances in Planar Lipid Bilayers and Liposomes. Vol. 11. Amsterdam, the Netherlands: Elsevier; 2010. pp. 101–126.
-
- Gongadze E, van Rienen U, Kralj-Iglič V, Iglič A. Langevin Poisson- Boltzmann equation: point-like ions and water dipoles near charged membrane surface. Gen Physiol Biophys. 2011;30:130–137. - PubMed
-
- Gouy MG. On the configuration of the electric charge at the electrolyt interface. J Physique. 1910;9:457–468. French.
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

