Adhesion of osteoblasts to a nanorough titanium implant surface
- PMID: 21931478
- PMCID: PMC3173045
- DOI: 10.2147/IJN.S21755
Adhesion of osteoblasts to a nanorough titanium implant surface
Abstract
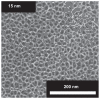
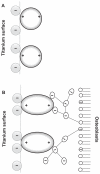
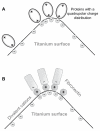
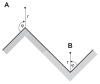
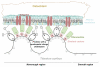
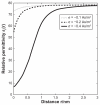
This work considers the adhesion of cells to a nanorough titanium implant surface with sharp edges. The basic assumption was that the attraction between the negatively charged titanium surface and a negatively charged osteoblast is mediated by charged proteins with a distinctive quadrupolar internal charge distribution. Similarly, cation-mediated attraction between fibronectin molecules and the titanium surface is expected to be more efficient for a high surface charge density, resulting in facilitated integrin mediated osteoblast adhesion. We suggest that osteoblasts are most strongly bound along the sharp convex edges or spikes of nanorough titanium surfaces where the magnitude of the negative surface charge density is the highest. It is therefore plausible that nanorough regions of titanium surfaces with sharp edges and spikes promote the adhesion of osteoblasts.
Keywords: adhesion; nanostructures; osteoblasts; osteointegration; titanium implants.
Figures


References
-
- Lüthen F, Lange R, Becker P, Rychly J, Beck U, Nebe B. The influence of surface roughness of titanium on 1-βand 3-βintegrin adhesion and the organization of fibronectin in human osteoblastic cells. Biomaterials. 2004;26:2423–2440. - PubMed
-
- Nebe B, Lüthen F, Lange R, Beck U. Interface interactions of osteoblasts with structured titanium and the correlation between physicochemical characteristics and cell biological parameters. Macromol Biosci. 2007;7:567–578. - PubMed
-
- Anselme K. Osteoblast adhesion on biomaterials. Biomaterials. 2000;21:667–681. - PubMed
-
- Anselme K, Bigerelle M, Noel B, et al. Qualitative and quantitative study of human osteoblast adhesion on materials with various surface roughness. J Biomed Mater Res. 2000;49:155–166. - PubMed
-
- Shelton RM, Rasmussen AC, Davies JE. Protein adsorption at the interface between charged polymer substrata and migrating osteoblasts. Biomaterials. 1998;9:24–29. - PubMed
Appendix references
-
- Lamperski S, Outhwaite CW. Volume term in the inhomogeneous Poisson-Boltzmann theory for high surface charge. Langmuir. 2002;18:3423–3424.
-
- Iglič A, Gongadze E, Bohinc K. Excluded volume effect and orientational ordering near charged surface in solution of ions and Langevin dipoles. Bioelectrochemistry. 2010;79:223–227. - PubMed
-
- Gongadze E, Bohinc K, van Rienen U, Kralj-Iglič V, Iglič A. Spatial variation of permittivity near a charged membrane in contact with electrolyte solution. In: Iglič A, editor. Advances in Planar Lipid Bilayers and Liposomes. Vol. 11. Amsterdam, the Netherlands: Elsevier; 2010. pp. 101–126.
-
- Gongadze E, van Rienen U, Kralj-Iglič V, Iglič A. Langevin Poisson- Boltzmann equation: point-like ions and water dipoles near charged membrane surface. Gen Physiol Biophys. 2011;30:130–137. - PubMed
-
- Gouy MG. On the configuration of the electric charge at the electrolyt interface. J Physique. 1910;9:457–468. French.
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

