Critical appraisal of pazopanib as treatment for patients with advanced metastatic renal cell carcinoma
- PMID: 21931501
- PMCID: PMC3173017
- DOI: 10.2147/CMR.S15557
Critical appraisal of pazopanib as treatment for patients with advanced metastatic renal cell carcinoma
Abstract
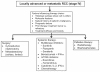
The management of renal cell carcinoma (RCC) has undergone significant changes during the past 10 years, with the treatment of metastatic RCC undergoing the most radical changes. These developments reflect an enhanced understanding of this tumor's underlying biology, which was then translated into the development of a new treatment paradigm. Current therapeutic approaches for the management of patients with metastatic RCC utilize knowledge of histology, molecular abnormalities, clinical prognostic factors, the natural history of this malignancy, and the treatment efficacy and toxicity of available agents. The treatment options available for patients with metastatic RCC have changed dramatically over the past 6 years. Interferon-α and interleukin-2 were the previous mainstays of therapy, but since December 2005, six new agents have been approved in the US for the treatment of advanced RCC. Three are multi-targeted tyrosine kinase inhibitors (TKI) including sunitinib, sorafenib, and pazopanib, two target the mammalian target of rapamycin (temsirolimus and everolimus), and one is a humanized monoclonal antibody (bevacizumab in combination with interferon-α). The current review focuses on the newest TKI available to treat patients with metastatic RCC, pazopanib. The development of this agent both preclinically and clinically is reviewed. The efficacy and safety data from the pivotal clinical trials are discussed, and the potential role of pazopanib in the treatment of patients with metastatic RCC in comparison to other treatment alternatives is critically appraised. This agent has a favorable overall risk benefit, and the available data demonstrate efficacy in patients with metastatic RCC who are either treatment-naïve or cytokine refractory. It therefore represents another alternative for treatment of metastatic RCC patients.
Keywords: metastatic; pazopanib; renal cell carcinoma.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Pazopanib: the newest tyrosine kinase inhibitor for the treatment of advanced or metastatic renal cell carcinoma.Drugs. 2011 Mar 5;71(4):443-54. doi: 10.2165/11588960-000000000-00000. Drugs. 2011. PMID: 21395357 Review.
-
The prospects of pazopanib in advanced renal cell carcinoma.Ther Adv Urol. 2013 Oct;5(5):223-32. doi: 10.1177/1756287213495099. Ther Adv Urol. 2013. PMID: 24082917 Free PMC article.
-
Pharmacotherapy options in advanced renal cell carcinoma: what role for pazopanib?Clin Med Insights Oncol. 2011;5:349-64. doi: 10.4137/CMO.S6087. Epub 2011 Nov 7. Clin Med Insights Oncol. 2011. PMID: 22174596 Free PMC article.
-
Optimal management of metastatic renal cell carcinoma: current status.Drugs. 2013 Apr;73(5):427-38. doi: 10.1007/s40265-013-0043-1. Drugs. 2013. PMID: 23572408 Review.
-
Systemic therapy for metastatic renal cell carcinoma in treatment naïve patients: a risk-based approach.Expert Opin Pharmacother. 2010 Oct;11(14):2351-62. doi: 10.1517/14656566.2010.499126. Expert Opin Pharmacother. 2010. PMID: 20586712 Review.
Cited by
-
Concise drug review: pazopanib and axitinib.Oncologist. 2012;17(8):1081-9. doi: 10.1634/theoncologist.2012-0055. Epub 2012 Jun 25. Oncologist. 2012. PMID: 22733795 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Jemal A, Siegel R, Xu J, Ward E. Cancer statistics, 2010. CA Cancer J Clin. 2010;60(5):277–300. - PubMed
-
- Ferlay J, Shin HR, Bray F, Forman D, Mathers C, Parkin DM International Agency for Research on Cancer. GLOBOCAN 2008. Cancer incidence and mortality worldwide: CancerBase. 2008. [Accessed June 21, 2011]. Available from: http://globocan.iarc.fr.
-
- Tsivian M, Moreira DM, Caso JR, Mouraviev V, Polascik TJ. Cigarette smoking is associated with advanced renal cell carcinoma. J Clin Oncol. 2011;29(15):2027–2031. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

