Clarifying the mechanism of superantigen toxicity
- PMID: 21931531
- PMCID: PMC3172192
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pbio.1001145
Clarifying the mechanism of superantigen toxicity
Conflict of interest statement
The author has declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
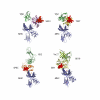
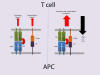
Similar articles
-
Superantigen antagonist blocks Th1 cytokine gene induction and lethal shock.J Leukoc Biol. 2001 Jun;69(6):921-7. J Leukoc Biol. 2001. PMID: 11404377
-
Increased mortality and impaired clonal deletion after staphylococcal enterotoxin B injection in old mice: relation to cytokines and nitric oxide production.Scand J Immunol. 1997 Nov;46(5):469-78. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-3083.1997.d01-153.x. Scand J Immunol. 1997. PMID: 9393629
-
Peptide antagonists of superantigen toxins.Mol Divers. 2004;8(2):113-20. doi: 10.1023/b:modi.0000025654.04427.44. Mol Divers. 2004. PMID: 15209162
-
The bacterial superantigen and superantigen-like proteins.Immunol Rev. 2008 Oct;225:226-43. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065X.2008.00681.x. Immunol Rev. 2008. PMID: 18837785 Review.
-
Microbial superantigens as virulence factors and ways to counteract their actions.Scand J Infect Dis. 2003;35(9):642-6. doi: 10.1080/00365540310016330. Scand J Infect Dis. 2003. PMID: 14620148 Review.
Cited by
-
Keratinocytes costimulate naive human T cells via CD2: a potential target to prevent the development of proinflammatory Th1 cells in the skin.Cell Mol Immunol. 2020 Apr;17(4):380-394. doi: 10.1038/s41423-019-0261-x. Epub 2019 Jul 19. Cell Mol Immunol. 2020. PMID: 31324882 Free PMC article.
-
Differences Between Pediatric and Adult T Cell Responses to In Vitro Staphylococcal Enterotoxin B Stimulation.Front Immunol. 2018 Mar 20;9:498. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2018.00498. eCollection 2018. Front Immunol. 2018. PMID: 29616025 Free PMC article.
-
Multivariate profiling of African green monkey and rhesus macaque T lymphocytes.Sci Rep. 2019 Mar 18;9(1):4834. doi: 10.1038/s41598-019-41209-x. Sci Rep. 2019. PMID: 30886198 Free PMC article.
-
Engineered pH-dependent recycling antibodies enhance elimination of Staphylococcal enterotoxin B superantigen in mice.MAbs. 2019 Feb/Mar;11(2):411-421. doi: 10.1080/19420862.2018.1545510. Epub 2018 Dec 11. MAbs. 2019. PMID: 30526311 Free PMC article.
-
Heat shock transcription factor 1 is activated as a consequence of lymphocyte activation and regulates a major proteostasis network in T cells critical for cell division during stress.J Immunol. 2013 Oct 15;191(8):4068-79. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1202831. Epub 2013 Sep 16. J Immunol. 2013. PMID: 24043900 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Kotb M, Fraser J. D, editors. Superantigens: molecular basis for their role in human diseases. Washington: ASM Press; 2008. 263
-
- Todd J, Fishaut M, Kapral F, Welch T. Toxic-shock syndrome associated with phage-group-I Staphylococci. Lancet. 1978;2:1116–1118. - PubMed
-
- Chesney P. J, Bergdoll M. S, Davis J. P, Vergeront J. M. The disease spectrum, epidemiology, and etiology of toxic-shock syndrome. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1984;38:315–338. - PubMed
-
- Miethke T, Duschek K, Wahl C, Heeg K, Wagner H. Pathogenesis of the toxic shock syndrome: T cell mediated lethal shock caused by the superantigen TSST-1. Eur J Immunol. 1993;23:1494–1500. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

