Genetic association for renal traits among participants of African ancestry reveals new loci for renal function
- PMID: 21931561
- PMCID: PMC3169523
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1002264
Genetic association for renal traits among participants of African ancestry reveals new loci for renal function
Abstract
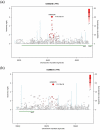
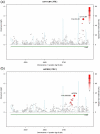
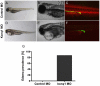
Chronic kidney disease (CKD) is an increasing global public health concern, particularly among populations of African ancestry. We performed an interrogation of known renal loci, genome-wide association (GWA), and IBC candidate-gene SNP association analyses in African Americans from the CARe Renal Consortium. In up to 8,110 participants, we performed meta-analyses of GWA and IBC array data for estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR), CKD (eGFR <60 mL/min/1.73 m(2)), urinary albumin-to-creatinine ratio (UACR), and microalbuminuria (UACR >30 mg/g) and interrogated the 250 kb flanking region around 24 SNPs previously identified in European Ancestry renal GWAS analyses. Findings were replicated in up to 4,358 African Americans. To assess function, individually identified genes were knocked down in zebrafish embryos by morpholino antisense oligonucleotides. Expression of kidney-specific genes was assessed by in situ hybridization, and glomerular filtration was evaluated by dextran clearance. Overall, 23 of 24 previously identified SNPs had direction-consistent associations with eGFR in African Americans, 2 of which achieved nominal significance (UMOD, PIP5K1B). Interrogation of the flanking regions uncovered 24 new index SNPs in African Americans, 12 of which were replicated (UMOD, ANXA9, GCKR, TFDP2, DAB2, VEGFA, ATXN2, GATM, SLC22A2, TMEM60, SLC6A13, and BCAS3). In addition, we identified 3 suggestive loci at DOK6 (p-value = 5.3×10(-7)) and FNDC1 (p-value = 3.0×10(-7)) for UACR, and KCNQ1 with eGFR (p = 3.6×10(-6)). Morpholino knockdown of kcnq1 in the zebrafish resulted in abnormal kidney development and filtration capacity. We identified several SNPs in association with eGFR in African Ancestry individuals, as well as 3 suggestive loci for UACR and eGFR. Functional genetic studies support a role for kcnq1 in glomerular development in zebrafish.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures

References
-
- Coresh J, Selvin E, Stevens LA, Manzi J, Kusek JW, et al. Prevalence of chronic kidney disease in the United States. JAMA. 2007;298:2038–2047. - PubMed
-
- Fox CS, Yang Q, Cupples LA, Guo CY, Larson MG, et al. Genomewide Linkage Analysis to Serum Creatinine, GFR, and Creatinine Clearance in a Community-Based Population: The Framingham Heart Study. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2004;15:2457–2461. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- N01-HB-73002/HB/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01-HB-72992/HB/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01-HC-25195/HC/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01-HB-97068/HB/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01-HB-97053/HB/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01-HB-72997/HB/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC045204/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC095095/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01-HC-45205/HC/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC055016/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01-HC-95162/HC/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01-HB-73003/HB/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC085080/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC095172/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC095161/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01-HC-05187/HC/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC095168/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- S06GM008016-380111/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC048048/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HL053916/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC055019/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL046380/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01-HL087660/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HL080295/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 AG062101/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- S06GM008016-320107/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- N01-HC-48047/HC/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC095169/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HL063463/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC085082/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01-HB-97064/HB/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01HL092577-01A1/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- M01RR00080/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- N01-HC-85081/HC/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL087660/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC055021/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01-HC-55022/HC/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL092577/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01-HC-95163/HC/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC015103/HC/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC085086/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01-HC-55016/HC/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01-HC-95168/HC/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC085083/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01-HB-97070/HB/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC048049/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01-HB-97056/HB/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01-HB-72982/HB/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- Z01 HG200362/ImNIH/Intramural NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC085085/HC/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01-HC-45204/HC/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01-HB-72993/HB/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01-HB-73000/HB/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01-HC-95159/HC/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC055015/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- 1R01AG032098-01A1/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC095167/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL076784/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01-HC-95095/HC/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01-HC-95165/HC/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01-HB-97085/HB/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 AG062106/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- N01-HC-55021/HC/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HL053938/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01-HC-85086/HC/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC095159/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01-HB-73005/HB/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01-HC-48050/HC/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HL064360/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC045205/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG032098/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC055020/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HL 46380/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01-HC-85082/HC/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01-HB-73006/HB/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268200782096C/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC-55222/HC/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01-HC-55019/HC/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HL077813/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC025195/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01-HB-97071/HB/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01-HB-97066/HB/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- Z01 AG000513/ImNIH/Intramural NIH HHS/United States
- N01-HC-55015/HC/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC055222/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 AG062103/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HL053941/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01-HC-95169/HC/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC095170/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01-HC-95164/HC/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01-HB-72995/HB/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01-HC-48049/HC/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01-HB-97051/HB/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01-HL-071205/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01-HB-97062/HB/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01-HC-85083/HC/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01-HC-75150/HC/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC045134/HC/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01-HC-55020/HC/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01-HB-73001/HB/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01-HC-85080/HC/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01-HB-97060/HB/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01-HC-95160/HC/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC005187/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC085079/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC095163/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC048047/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01-HC-95171/HC/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01-HB-97073/HB/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC055018/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- M01 RR010284/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- N01-HB-97054/HB/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HL053934/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HL063429/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01-HC-95172/HC/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01-HB-72994/HB/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC085084/HC/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC048050/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL071205/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01-HB-72991/HB/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01-HB-97072/HB/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC055022/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01-HC-95100/HC/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01-HC-85079/HC/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01-HC-95161/HC/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC095166/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01-HB-97058/HB/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC095162/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HL053937/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01-HC-48048/HC/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC095171/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01-HB-72996/HB/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC075150/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01-HC-55018/HC/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG028321/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- N01-HC-95166/HC/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- 2M01RR010284/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- N01-HB-97061/HB/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC065226/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC095165/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- M01 RR000080/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC045133/HC/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC095164/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01-HB-73004/HB/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01-HC-95170/HC/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01-HB-72998/HB/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC035129/HC/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC085081/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01-HB-97069/HB/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01-HC-95167/HC/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01-HC-65226/HC/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC095160/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

