cIAP1/2 are direct E3 ligases conjugating diverse types of ubiquitin chains to receptor interacting proteins kinases 1 to 4 (RIP1-4)
- PMID: 21931591
- PMCID: PMC3171409
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0022356
cIAP1/2 are direct E3 ligases conjugating diverse types of ubiquitin chains to receptor interacting proteins kinases 1 to 4 (RIP1-4)
Abstract
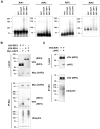
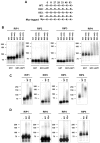
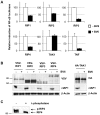
The RIP kinases have emerged as essential mediators of cellular stress that integrate both extracellular stimuli emanating from various cell-surface receptors and signals coming from intracellular pattern recognition receptors. The molecular mechanisms regulating the ability of the RIP proteins to transduce the stress signals remain poorly understood, but seem to rely only partially on their kinase activities. Recent studies on RIP1 and RIP2 have highlighted the importance of ubiquitination as a key process regulating their capacity to activate downstream signaling pathways. In this study, we found that XIAP, cIAP1 and cIAP2 not only directly bind to RIP1 and RIP2 but also to RIP3 and RIP4. We show that cIAP1 and cIAP2 are direct E3 ubiquitin ligases for all four RIP proteins and that cIAP1 is capable of conjugating the RIPs with diverse types of ubiquitin chains, including linear chains. Consistently, we show that repressing cIAP1/2 levels affects the activation of NF-κB that is dependent on RIP1, -2, -3 and -4. Finally, we identified Lys51 and Lys145 of RIP4 as two critical residues for cIAP1-mediated ubiquitination and NF-κB activation.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures


References
-
- Meylan E, Tschopp J. The RIP kinases: crucial integrators of cellular stress. Trends Biochem Sci. 2005;30:151–159. - PubMed
-
- Cusson-Hermance N, Khurana S, Lee TH, Fitzgerald KA, Kelliher MA. Rip1 mediates the Trif-dependent toll-like receptor 3- and 4-induced NF-{kappa}B activation but does not contribute to interferon regulatory factor 3 activation. J Biol Chem. 2005;280:36560–36566. - PubMed
-
- Meylan E, Burns K, Hofmann K, Blancheteau V, Martinon F, et al. RIP1 is an essential mediator of Toll-like receptor 3-induced NF-kappa B activation. Nat Immunol. 2004;5:503–507. - PubMed
-
- Janssens S, Tinel A, Lippens S, Tschopp J. PIDD mediates NF-kappaB activation in response to DNA damage. Cell. 2005;123:1079–1092. - PubMed
-
- Park JH, Kim YG, McDonald C, Kanneganti TD, Hasegawa M, et al. RICK/RIP2 mediates innate immune responses induced through Nod1 and Nod2 but not TLRs. J Immunol. 2007;178:2380–2386. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

