Disruption of Yarrowia lipolytica TPS1 gene encoding trehalose-6-P synthase does not affect growth in glucose but impairs growth at high temperature
- PMID: 21931609
- PMCID: PMC3171402
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0023695
Disruption of Yarrowia lipolytica TPS1 gene encoding trehalose-6-P synthase does not affect growth in glucose but impairs growth at high temperature
Abstract
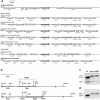
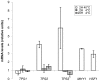
We have cloned the Yarrowia lipolytica TPS1 gene encoding trehalose-6-P synthase by complementation of the lack of growth in glucose of a Saccharomyces cerevisiae tps1 mutant. Disruption of YlTPS1 could only be achieved with a cassette placed in the 3' half of its coding region due to the overlap of its sequence with the promoter of the essential gene YlTFC1. The Yltps1 mutant grew in glucose although the Y. lipolytica hexokinase is extremely sensitive to inhibition by trehalose-6-P. The presence of a glucokinase, insensitive to trehalose-6-P, that constitutes about 80% of the glucose phosphorylating capacity during growth in glucose may account for the growth phenotype. Trehalose content was below 1 nmol/mg dry weight in Y. lipolytica, but it increased in strains expressing YlTPS1 under the control of the YlTEF1 promoter or with a disruption of YALI0D15598 encoding a putative trehalase. mRNA levels of YlTPS1 were low and did not respond to thermal stresses, but that of YlTPS2 (YALI0D14476) and YlTPS3 (YALI0E31086) increased 4 and 6 times, repectively, by heat treatment. Disruption of YlTPS1 drastically slowed growth at 35°C. Homozygous Yltps1 diploids showed a decreased sporulation frequency that was ascribed to the low level of YALI0D20966 mRNA an homolog of the S. cerevisiae MCK1 which encodes a protein kinase that activates early meiotic gene expression.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures


References
-
- Elbein AD, Pan YT, Pastuszak I, Carroll D. New insights on trehalose: a multifunctional molecule. Glycobiology. 2003;13:17–27. - PubMed
-
- Gancedo C, Flores CL. The importance of a functional trehalose biosynthetic pathway for the life of yeasts and fungi. FEMS Yeast Res. 2004;4:351–359. - PubMed
-
- Cabib E, Leloir LF. The biosyntesis of trehalose phosphate. J Biol Chem. 1958;231:259–275. - PubMed
-
- Bell W, Klaassen P, Ohnacker M, Boller T, Herweijer M, et al. Characterization of the 56-kDa subunit of yeast trehalose-6-phosphate synthase and cloning of its gene reveal its identity with the product of CIF1, a regulator of carbon catabolite inactivation. Eur J Biochem. 1992;209:951–959. - PubMed
-
- De Virgilio C, Burckert N, Bell W, Jeno P, Boller T, et al. Disruption of TPS2, the gene encoding the 100-kDa subunit of the trehalose-6-phosphate synthase/phosphatase complex in Saccharomyces cerevisiae, causes accumulation of trehalose-6-phosphate and loss of trehalose-6-phosphate phosphatase activity. Eur J Biochem. 1993;212:315–323. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions

