Selection in coastal Synechococcus (cyanobacteria) populations evaluated from environmental metagenomes
- PMID: 21931665
- PMCID: PMC3170327
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0024249
Selection in coastal Synechococcus (cyanobacteria) populations evaluated from environmental metagenomes
Abstract
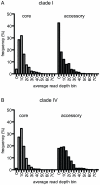
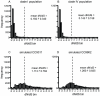
Environmental metagenomics provides snippets of genomic sequences from all organisms in an environmental sample and are an unprecedented resource of information for investigating microbial population genetics. Current analytical methods, however, are poorly equipped to handle metagenomic data, particularly of short, unlinked sequences. A custom analytical pipeline was developed to calculate dN/dS ratios, a common metric to evaluate the role of selection in the evolution of a gene, from environmental metagenomes sequenced using 454 technology of flow-sorted populations of marine Synechococcus, the dominant cyanobacteria in coastal environments. The large majority of genes (98%) have evolved under purifying selection (dN/dS<1). The metagenome sequence coverage of the reference genomes was not uniform and genes that were highly represented in the environment (i.e. high read coverage) tended to be more evolutionarily conserved. Of the genes that may have evolved under positive selection (dN/dS>1), 77 out of 83 (93%) were hypothetical. Notable among annotated genes, ribosomal protein L35 appears to be under positive selection in one Synechococcus population. Other annotated genes, in particular a possible porin, a large-conductance mechanosensitive channel, an ATP binding component of an ABC transporter, and a homologue of a pilus retraction protein had regions of the gene with elevated dN/dS. With the increasing use of next-generation sequencing in metagenomic investigations of microbial diversity and ecology, analytical methods need to accommodate the peculiarities of these data streams. By developing a means to analyze population diversity data from these environmental metagenomes, we have provided the first insight into the role of selection in the evolution of Synechococcus, a globally significant primary producer.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures





References
-
- Lo I, Denef VJ, VerBerkmoes NC, Shah MB, Goltsman D, et al. Strain-resolved community proteomics reveals recombining genomes of acidophilic bacteria. Nature. 2007;446:537–541. - PubMed
-
- Hewson I, Paerl RW, Tripp HJ, Zehr JP, Karl DM. Metagenomic potential of microbial assemblages in the surface waters of the central Pacific Ocean tracks variability in oceanic habitat. Limnology and Oceanography. 2009;54:1981–1994.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

