A novel compound C12 inhibits inflammatory cytokine production and protects from inflammatory injury in vivo
- PMID: 21931698
- PMCID: PMC3169595
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0024377
A novel compound C12 inhibits inflammatory cytokine production and protects from inflammatory injury in vivo
Abstract
Inflammation is a hallmark of many diseases. Although steroids and cyclooxygenase inhibitors are main anti-inflammatory therapeutical agents, they may cause serious side effects. Therefore, developing non-steroid anti-inflammatory agents is urgently needed. A novel hydrosoluble compound, C12 (2,6-bis(4-(3-(dimethylamino)-propoxy)benzylidene)cyclohexanone), has been designed and synthesized as an anti-inflammatory agent in our previous study. In the present study, we investigated whether C12 can affect inflammatory processes in vitro and in vivo. In mouse primary peritoneal macrophages, C12 potently inhibited the production of the proinflammatory gene expression including TNF-α, IL-1β, IL-6, iNOS, COX-2 and PGE synthase. The activity of C12 was partly dependent on inhibition of ERK/JNK (but p38) phosphorylation and NF-κB activation. In vivo, C12 suppressed proinflammatory cytokine production in plasma and liver, attenuated lung histopathology, and significantly reduced mortality in endotoxemic mice. In addition, the pre-treatment with C12 reduced the inflammatory pain in the acetic acid and formalin models and reduced the carrageenan-induced paw oedema and acetic acid-increased vascular permeability. Taken together, C12 has multiple anti-inflammatory effects. These findings, coupled with the low toxicity and hydrosolubility of C12, suggests that this agent may be useful in the treatment of inflammatory diseases.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
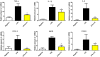
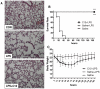
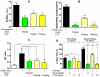
Similar articles
-
Stauntoside B inhibits macrophage activation by inhibiting NF-κB and ERK MAPK signalling.Pharmacol Res. 2016 Sep;111:303-315. doi: 10.1016/j.phrs.2016.06.022. Epub 2016 Jun 22. Pharmacol Res. 2016. PMID: 27343699
-
Anti-inflammatory effect of tetrahydrocoptisine from Corydalis impatiens is a function of possible inhibition of TNF-α, IL-6 and NO production in lipopolysaccharide-stimulated peritoneal macrophages through inhibiting NF-κB activation and MAPK pathway.Eur J Pharmacol. 2013 Sep 5;715(1-3):62-71. doi: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2013.06.017. Epub 2013 Jun 25. Eur J Pharmacol. 2013. PMID: 23810685
-
Inhibition of high glucose-induced inflammatory response and macrophage infiltration by a novel curcumin derivative prevents renal injury in diabetic rats.Br J Pharmacol. 2012 Jun;166(3):1169-82. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.2012.01854.x. Br J Pharmacol. 2012. PMID: 22242942 Free PMC article.
-
Attenuation of Inflammatory Symptoms by Icariside B2 in Carrageenan and LPS-Induced Inflammation Models via Regulation of MAPK/NF-κB Signaling Cascades.Biomolecules. 2020 Jul 11;10(7):1037. doi: 10.3390/biom10071037. Biomolecules. 2020. PMID: 32664577 Free PMC article.
-
Potent anti-inflammatory effect of a novel furan-2,5-dione derivative, BPD, mediated by dual suppression of COX-2 activity and LPS-induced inflammatory gene expression via NF-κB inactivation.Br J Pharmacol. 2012 Mar;165(6):1926-1940. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.2011.01670.x. Br J Pharmacol. 2012. PMID: 21913901 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Anti-Inflammatory Effect of Rhapontici Radix Ethanol Extract via Inhibition of NF-κB and MAPK and Induction of HO-1 in Macrophages.Mediators Inflamm. 2016;2016:7216912. doi: 10.1155/2016/7216912. Epub 2016 Jul 25. Mediators Inflamm. 2016. PMID: 27524868 Free PMC article.
-
Anti-Inflammatory Effects of Melandrii Herba Ethanol Extract via Inhibition of NF-κB and MAPK Signaling Pathways and Induction of HO-1 in RAW 264.7 Cells and Mouse Primary Macrophages.Molecules. 2016 Jun 22;21(6):818. doi: 10.3390/molecules21060818. Molecules. 2016. PMID: 27338335 Free PMC article.
-
Attenuation of vincristine-induced neuropathy by synthetic cyclohexenone-functionalized derivative in mice model.Neurol Sci. 2019 Sep;40(9):1799-1811. doi: 10.1007/s10072-019-03884-6. Epub 2019 Apr 30. Neurol Sci. 2019. PMID: 31041611
-
Sulfated derivative of 20(S)-ginsenoside Rh2 inhibits inflammatory cytokines through MAPKs and NF-kappa B pathways in LPS-induced RAW264.7 macrophages.Inflammation. 2012 Oct;35(5):1659-68. doi: 10.1007/s10753-012-9482-1. Inflammation. 2012. PMID: 22614119
-
WMJ-S-001, a novel aliphatic hydroxamate derivative, exhibits anti-inflammatory properties via MKP-1 in LPS-stimulated RAW264.7 macrophages.Br J Pharmacol. 2015 Apr;172(7):1894-908. doi: 10.1111/bph.13040. Epub 2015 Feb 27. Br J Pharmacol. 2015. PMID: 25521622 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Brevetti G, Giugliano G, Brevetti L, Hiatt WR. Inflammation in peripheral artery disease. Circulation. 2010;122:1862–1875. - PubMed
-
- Hummasti S, Hotamisligil GS. Endoplasmic reticulum stress and inflammation in obesity and diabetes. Circ Res. 2010;107:579–591. - PubMed
-
- Lambrecht BN, Hammad H. The role of dendritic and epithelial cells as master regulators of allergic airway inflammation. Lancet. 2010;376:835–843. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

