Global patterns of bacterial beta-diversity in seafloor and seawater ecosystems
- PMID: 21931760
- PMCID: PMC3169623
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0024570
Global patterns of bacterial beta-diversity in seafloor and seawater ecosystems
Abstract
Background: Marine microbial communities have been essential contributors to global biomass, nutrient cycling, and biodiversity since the early history of Earth, but so far their community distribution patterns remain unknown in most marine ecosystems.
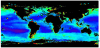
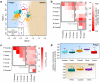
Methodology/principal findings: The synthesis of 9.6 million bacterial V6-rRNA amplicons for 509 samples that span the global ocean's surface to the deep-sea floor shows that pelagic and benthic communities greatly differ, at all taxonomic levels, and share <10% bacterial types defined at 3% sequence similarity level. Surface and deep water, coastal and open ocean, and anoxic and oxic ecosystems host distinct communities that reflect productivity, land influences and other environmental constraints such as oxygen availability. The high variability of bacterial community composition specific to vent and coastal ecosystems reflects the heterogeneity and dynamic nature of these habitats. Both pelagic and benthic bacterial community distributions correlate with surface water productivity, reflecting the coupling between both realms by particle export. Also, differences in physical mixing may play a fundamental role in the distribution patterns of marine bacteria, as benthic communities showed a higher dissimilarity with increasing distance than pelagic communities.
Conclusions/significance: This first synthesis of global bacterial distribution across different ecosystems of the World's oceans shows remarkable horizontal and vertical large-scale patterns in bacterial communities. This opens interesting perspectives for the definition of biogeographical biomes for bacteria of ocean waters and the seabed.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures



References
-
- Giovannoni SJ, Stingl U. Molecular diversity and ecology of microbial plankton. Nature. 2005;309:343–348. - PubMed
-
- Azam F, Malfatti F. Microbial structuring of marine ecosystems. Nat Rev Microbiol. 2007;5:782–791. - PubMed
-
- Falkowski PG, Fenchel T, Delong EF. The microbial engines that drive Earth's biogeochemical cycles. Science. 2008;320:1034–1039. - PubMed

