Resveratrol suppresses constitutive activation of AKT via generation of ROS and induces apoptosis in diffuse large B cell lymphoma cell lines
- PMID: 21931821
- PMCID: PMC3171480
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0024703
Resveratrol suppresses constitutive activation of AKT via generation of ROS and induces apoptosis in diffuse large B cell lymphoma cell lines
Abstract
Background: We have recently shown that deregulation PI3-kinase/AKT survival pathway plays an important role in pathogenesis of diffuse large B cell lymphoma (DLBCL). In an attempt to identify newer therapeutic agents, we investigated the role of Resveratrol (trans-3,4', 5-trihydroxystilbene), a naturally occurring polyphenolic compound on a panel of diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL) cells in causing inhibition of cell viability and inducing apoptosis.
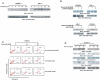
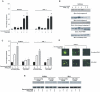
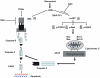
Methodology/principal findings: We investigated the action of Resveratrol on DLBCL cells and found that Resveratrol inhibited cell viability and induced apoptosis by inhibition of constitutively activated AKT and its downstream targets via generation of reactive oxygen species (ROS). Simultaneously, Resveratrol treatment of DLBCL cell lines also caused ROS dependent upregulation of DR5; and interestingly, co-treatment of DLBCL with sub-toxic doses of TRAIL and Resveratrol synergistically induced apoptosis via utilizing DR5, on the other hand, gene silencing of DR5 abolished this effect.
Conclusion/significance: Altogether, these data suggest that Resveratrol acts as a suppressor of AKT/PKB pathway leading to apoptosis via generation of ROS and at the same time primes DLBCL cells via up-regulation of DR5 to TRAIL-mediated apoptosis. These data raise the possibility that Resveratrol may have a future therapeutic role in DLBCL and possibly other malignancies with constitutive activation of the AKT/PKB pathway.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
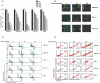
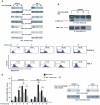
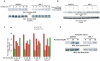
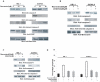
Similar articles
-
The multiple mechanisms of cell death triggered by resveratrol in lymphoma and leukemia.Int J Mol Sci. 2014 Mar 20;15(3):4977-93. doi: 10.3390/ijms15034977. Int J Mol Sci. 2014. PMID: 24658441 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Akt inhibitors MK-2206 and nelfinavir overcome mTOR inhibitor resistance in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma.Clin Cancer Res. 2012 May 1;18(9):2534-44. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-11-1407. Epub 2012 Feb 14. Clin Cancer Res. 2012. PMID: 22338016 Free PMC article.
-
Phosphorylated IκBα predicts poor prognosis in activated B-cell lymphoma and its inhibition with thymoquinone induces apoptosis via ROS release.PLoS One. 2013;8(3):e60540. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0060540. Epub 2013 Mar 28. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 23555990 Free PMC article.
-
The Bruton tyrosine kinase (BTK) inhibitor PCI-32765 synergistically increases proteasome inhibitor activity in diffuse large-B cell lymphoma (DLBCL) and mantle cell lymphoma (MCL) cells sensitive or resistant to bortezomib.Br J Haematol. 2013 Apr;161(1):43-56. doi: 10.1111/bjh.12206. Epub 2013 Jan 30. Br J Haematol. 2013. PMID: 23360303 Free PMC article.
-
Prognostic significance of XIAP expression in DLBCL and effect of its inhibition on AKT signalling.J Pathol. 2010 Oct;222(2):180-90. doi: 10.1002/path.2747. J Pathol. 2010. PMID: 20632385
Cited by
-
The multiple mechanisms of cell death triggered by resveratrol in lymphoma and leukemia.Int J Mol Sci. 2014 Mar 20;15(3):4977-93. doi: 10.3390/ijms15034977. Int J Mol Sci. 2014. PMID: 24658441 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Bibliometric and visualized analysis of resveratrol in anticancer investigations.Food Sci Nutr. 2024 Jan 6;12(4):2223-2239. doi: 10.1002/fsn3.3932. eCollection 2024 Apr. Food Sci Nutr. 2024. PMID: 38628201 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Repeated Administration of Resveratrol Has Measurable Effects on Circulating T-Cell Subsets in Humans.Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2017;2017:6781872. doi: 10.1155/2017/6781872. Epub 2017 May 4. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2017. PMID: 28546852 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Novel derivative of aminobenzenesulfonamide (3c) induces apoptosis in colorectal cancer cells through ROS generation and inhibits cell migration.BMC Cancer. 2017 Jan 3;17(1):4. doi: 10.1186/s12885-016-3005-7. BMC Cancer. 2017. PMID: 28049506 Free PMC article.
-
Deguelin induces the apoptosis of lung cancer cells through regulating a ROS driven Akt pathway.Cancer Cell Int. 2015 Feb 25;15:25. doi: 10.1186/s12935-015-0166-4. eCollection 2015. Cancer Cell Int. 2015. PMID: 25741219 Free PMC article.
References
-
- American Society of Hematology. A clinical evaluation of the International Lymphoma Study Group classification of non-Hodgkin's lymphoma. The Non-Hodgkin's Lymphoma Classification Project. Blood. 1997;89:3909–3918. - PubMed
-
- Escalon MP, Lossos IS. Pharmacotherapy of large B-cell lymphoma. Expert Opin Pharmacother. 2008;9:2247–2258. - PubMed
-
- Fisher RI. Cyclophosphamide, doxorubicin, vincristine, and prednisone versus intensive chemotherapy in non-Hodgkin's lymphoma. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol. 1997;40(Suppl):S42–46. - PubMed
-
- Uddin S, Hussain AR, Ahmed M, Abubaker J, Al-Sanea N, et al. High prevalence of fatty acid synthase expression in colorectal cancers in Middle Eastern patients and its potential role as a therapeutic target. Am J Gastroenterol. 2009;104:1790–1801. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

