Induction of heat shock proteins by hyperthermia and noise overstimulation in hsf1 -/- mice
- PMID: 21932106
- PMCID: PMC3254713
- DOI: 10.1007/s10162-011-0289-9
Induction of heat shock proteins by hyperthermia and noise overstimulation in hsf1 -/- mice
Abstract
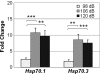
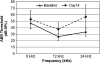
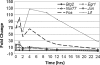
Diverse cellular and environmental stresses can activate the heat shock response, an evolutionarily conserved mechanism to protect proteins from denaturation. Stressors activate heat shock transcription factor 1 (HSF1), which binds to heat shock elements in the genes for heat shock proteins, leading to rapid induction of these important molecular chaperones. Both heat and noise stress are known to activate the heat shock response in the cochlea and protect it from subsequent noise trauma. However, the contribution of HSF1 to induction of heat shock proteins following noise trauma has not been investigated at the molecular level. We evaluated the role of HSF1 in the cochlea following noise stress by examining induction of heat shock proteins in Hsf1 ( +/- ) control and Hsf1 ( -/- ) mice. Heat stress rapidly induced expression of Hsp25, Hsp47, Hsp70.1, Hsp70.3, Hsp84, Hsp86, and Hsp110 in the cochleae of wild-type and Hsf1 ( +/- ) mice, but not in Hsf1 ( -/- ) mice, confirming the essential role of HSF1 in mediating the heat shock response. Exposure to broadband noise (2-20 kHz) at 106 dB SPL for 2 h produced partial hearing loss. Maximal induction of heat shock proteins occurred 4 h after the noise. In comparison to heat stress, noise stress resulted in lower induced levels of Hsp25, Hsp70.1, Hsp70.3, Hsp86, and Hsp110 in Hsf1 ( +/- ) mice. Induction of these heat shock proteins was attenuated, but not completely eliminated, in Hsf1 ( -/- ) mice. These same noise exposure conditions induced genes for several immediate early transcription factors and maximum induction occurred earlier than for heat shock proteins. Thus, additional signaling pathways and transcriptional regulators that are activated by noise probably contribute to induction of heat shock proteins in the cochlea.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Heat shock factor 1-deficient mice exhibit decreased recovery of hearing following noise overstimulation.J Neurosci Res. 2005 Aug 15;81(4):589-96. doi: 10.1002/jnr.20417. J Neurosci Res. 2005. PMID: 15952177
-
Transcriptional regulation and binding of heat shock factor 1 and heat shock factor 2 to 32 human heat shock genes during thermal stress and differentiation.Cell Stress Chaperones. 2004 Mar;9(1):21-8. doi: 10.1379/481.1. Cell Stress Chaperones. 2004. PMID: 15270074 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular chaperones as HSF1-specific transcriptional repressors.Genes Dev. 1998 Mar 1;12(5):654-66. doi: 10.1101/gad.12.5.654. Genes Dev. 1998. PMID: 9499401 Free PMC article.
-
Heat shock proteins and heat shock factor 1 in carcinogenesis and tumor development: an update.Arch Toxicol. 2013 Jan;87(1):19-48. doi: 10.1007/s00204-012-0918-z. Epub 2012 Aug 11. Arch Toxicol. 2013. PMID: 22885793 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Is there a role for HSF1 in viral infections?FEBS Open Bio. 2022 Jun;12(6):1112-1124. doi: 10.1002/2211-5463.13419. Epub 2022 May 10. FEBS Open Bio. 2022. PMID: 35485710 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Blockade of PI3K/AKT pathway enhances sensitivity of Raji cells to chemotherapy through down-regulation of HSP70.Cancer Cell Int. 2013 May 24;13(1):48. doi: 10.1186/1475-2867-13-48. Cancer Cell Int. 2013. PMID: 23706027 Free PMC article.
-
Heat shock protein 70 (Hsp70) inhibits oxidative phosphorylation and compensates ATP balance through enhanced glycolytic activity.J Appl Physiol (1985). 2012 Dec 1;113(11):1669-76. doi: 10.1152/japplphysiol.00658.2012. Epub 2012 Oct 4. J Appl Physiol (1985). 2012. PMID: 23042904 Free PMC article.
-
Environmental stress and hypertension: the disregarded role of HSP70.J Hum Hypertens. 2024 Jun;38(6):538-541. doi: 10.1038/s41371-024-00917-2. Epub 2024 May 21. J Hum Hypertens. 2024. PMID: 38773240 Review. No abstract available.
-
Selective hair cell ablation and noise exposure lead to different patterns of changes in the cochlea and the cochlear nucleus.Neuroscience. 2016 Sep 22;332:242-57. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2016.07.001. Epub 2016 Jul 9. Neuroscience. 2016. PMID: 27403879 Free PMC article.
-
Heat shock response in noise-induced hearing loss: effects of alanyl-glutamine dipeptide supplementation on heat shock proteins status.Braz J Otorhinolaryngol. 2020 Nov-Dec;86(6):703-710. doi: 10.1016/j.bjorl.2019.04.012. Epub 2019 Jun 8. Braz J Otorhinolaryngol. 2020. PMID: 31255578 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

