Efficacy and safety of monthly oral minodronate in patients with involutional osteoporosis
- PMID: 21932114
- PMCID: PMC3353114
- DOI: 10.1007/s00198-011-1782-z
Efficacy and safety of monthly oral minodronate in patients with involutional osteoporosis
Abstract
Monthly minodronate at 30 or 50 mg had similar efficacy as 1 mg daily in terms of change in bone mineral density (BMD) and bone turnover markers with similar safety profiles. This new regimen provides patients with a new option for taking minodronate.
Introduction: Minodronate at a daily oral dose of 1 mg has been proven to have antivertebral fracture efficacy. In the present study, the efficacy and safety of oral minodronate at monthly doses of either 30 mg or 50 mg were compared with a daily dose of 1 mg.
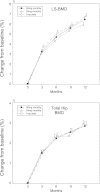
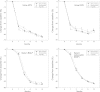
Methods: A total of 692 patients with involutional osteoporosis were randomized to receive minodronate at either 30 or 50 mg monthly or a daily dose of 1 mg. The primary endpoint was the percent change from baseline in lumbar spine (LS) BMD at 12 months. Total hip BMD, bone turnover markers, serum calcium (Ca), and parathyroid hormone (PTH) levels were also evaluated.
Results: Minodronate at monthly doses of 30 or 50 mg were noninferior to the 1 mg daily dose in terms of change in LS-BMD. Changes in total hip BMD were also comparable. Although a transient decrease in serum Ca and increase in PTH levels were observed in all three groups at slightly different magnitudes and time courses, changes in bone turnover markers were comparable among the different dosage groups with a similar time course. Safety profiles were also comparable.
Conclusion: Minodronate at monthly doses of 30 or 50 mg has similar efficacy to the daily 1 mg dose in terms of BMD and bone turnover markers with similar tolerability.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Effects of once-monthly minodronate versus risedronate in osteoporosis patients with rheumatoid arthritis: a 12-month randomized head-to-head comparison.Osteoporos Int. 2018 Jul;29(7):1637-1642. doi: 10.1007/s00198-018-4494-9. Epub 2018 Mar 24. Osteoporos Int. 2018. PMID: 29574518 Clinical Trial.
-
Effect of daily oral minodronate on vertebral fractures in Japanese postmenopausal women with established osteoporosis: a randomized placebo-controlled double-blind study.Osteoporos Int. 2009 Aug;20(8):1429-37. doi: 10.1007/s00198-008-0816-7. Epub 2008 Dec 20. Osteoporos Int. 2009. PMID: 19101754 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Efficacy and tolerability of once-monthly oral ibandronate (150 mg) and once-weekly oral alendronate (70 mg): additional results from the Monthly Oral Therapy With Ibandronate For Osteoporosis Intervention (MOTION) study.Clin Ther. 2009 Apr;31(4):751-61. doi: 10.1016/j.clinthera.2009.04.018. Clin Ther. 2009. PMID: 19446148 Clinical Trial.
-
Once-monthly dosing: an effective step forward.Bone. 2006 Apr;38(4 Suppl 1):S18-22. doi: 10.1016/j.bone.2006.01.153. Epub 2006 Mar 13. Bone. 2006. PMID: 16533625 Review.
-
Once-monthly ibandronate for postmenopausal osteoporosis: review of a new dosing regimen.Clin Ther. 2006 Apr;28(4):475-90. doi: 10.1016/j.clinthera.2006.04.006. Clin Ther. 2006. PMID: 16750461 Review.
Cited by
-
Monthly minodronate inhibits bone resorption to a greater extent than does monthly risedronate.Osteoporos Sarcopenia. 2016 Sep;2(3):170-174. doi: 10.1016/j.afos.2016.07.002. Epub 2016 Aug 3. Osteoporos Sarcopenia. 2016. PMID: 30775483 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of once-monthly minodronate versus risedronate in osteoporosis patients with rheumatoid arthritis: a 12-month randomized head-to-head comparison.Osteoporos Int. 2018 Jul;29(7):1637-1642. doi: 10.1007/s00198-018-4494-9. Epub 2018 Mar 24. Osteoporos Int. 2018. PMID: 29574518 Clinical Trial.
-
Patient preference for monthly bisphosphonate versus weekly bisphosphonate in a cluster-randomized, open-label, crossover trial: Minodroate Alendronate/Risedronate Trial in Osteoporosis (MARTO).J Bone Miner Metab. 2016 Mar;34(2):201-8. doi: 10.1007/s00774-015-0653-7. Epub 2015 Mar 21. J Bone Miner Metab. 2016. PMID: 25794468 Clinical Trial.
-
Study design of multi-center, open-label randomized controlled, head-to-head trial comparing minodronic acid and raloxifene: Japanese Osteoporosis Intervention Trial (JOINT)-04.J Bone Miner Metab. 2019 May;37(3):491-495. doi: 10.1007/s00774-018-0942-z. Epub 2018 Jul 17. J Bone Miner Metab. 2019. PMID: 30019249
-
Short-term bisphosphonate treatment reduces serum 25(OH) vitamin D3 and alters values of parathyroid hormone, pentosidine, and bone metabolic markers.Ther Clin Risk Manag. 2017 Feb 13;13:161-168. doi: 10.2147/TCRM.S120749. eCollection 2017. Ther Clin Risk Manag. 2017. PMID: 28243105 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Hagino H, Nishizawa Y, Sone T, Morii H, Taketani Y, Nakamura T, Itabashi A, Mizunuma H, Ohashi Y, Shiraki M, Minamide T, Matsumoto T. A double-blinded head-to-head trial of minodronate and alendronate in women with postmenopausal osteoporosis. Bone. 2009;44:1078–1084. doi: 10.1016/j.bone.2009.02.016. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Matsumoto T, Hagino H, Shiraki M, Fukunaga M, Nakano T, Takaoka K, Morii H, Ohashi Y, Nakamura T. Effect of daily oral minodronate on vertebral fractures in Japanese postmenopausal women with established osteoporosis: a randomized placebo-controlled double-blind study. Osteoporos Int. 2009;20:1429–1437. doi: 10.1007/s00198-008-0816-7. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Rizzoli R, Greenspan SL, Bone G, 3rd, Schnitzer TJ, Watts NB, Adami S, Foldes AJ, Roux C, Levine MA, Uebelhart B, Santora AC, 2nd, Kaur A, Peverly CA, Orloff JJ. Two-year results of once-weekly administration of alendronate 70 mg for the treatment of postmenopausal osteoporosis. J Bone Miner Res. 2002;17:1988–1996. doi: 10.1359/jbmr.2002.17.11.1988. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Uchida S, Taniguchi T, Shimizu T, Kakikawa T, Okuyama K, Okaniwa M, Arizono H, Nagata K, Santora AC, Shiraki M, Fukunaga M, Tomomitsu T, Ohashi Y, Nakamura T. Therapeutic effects of alendronate 35 mg once weekly and 5 mg once daily in Japanese patients with osteoporosis: a double-blind, randomized study. J Bone Miner Metab. 2005;23:382–388. doi: 10.1007/s00774-005-0616-5. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

