Association of the GALNT2 gene polymorphisms and several environmental factors with serum lipid levels in the Mulao and Han populations
- PMID: 21933382
- PMCID: PMC3196710
- DOI: 10.1186/1476-511X-10-160
Association of the GALNT2 gene polymorphisms and several environmental factors with serum lipid levels in the Mulao and Han populations
Abstract
Background: The association of UDP-N-acetyl-alpha-D-galactosamine: polypeptide N-acetylgalactosaminyltransferase 2 gene (GALNT2) single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) and serum lipid profiles in the general population is not well known. The present study was undertaken to detect the association of GALNT2 polymorphisms and several environmental factors with serum lipid levels in the Guangxi Mulao and Han populations.
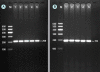
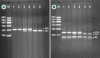
Method: A total of 775 subjects of Mulao nationality and 699 participants of Han nationality were randomly selected from our stratified randomized cluster samples. Genotyping of the GALNT2 rs2144300 and rs4846914 SNPs was performed by polymerase chain reaction and restriction fragment length polymorphism combined with gel electrophoresis, and then confirmed by direct sequencing.
Results: There were no significant differences in the genotypic and allelic frequencies of both SNPs between the two ethnic groups, or between the males and females. The subjects with TT genotype of rs2144300 in Mulao had lower serum triglyceride (TG) levels than the subjects with CC genotype in females (P < 0.01). The participants with CT/TT genotype of rs2144300 in Han had lower TG and apolipoprotein (Apo) B levels, and higher high-density lipoprotein cholesterol (HDL-C), ApoA1 levels and the ratio of ApoA1 to ApoB in males; and higher low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-C) and ApoB levels in females than the participants with CC genotype (P < 0.05-0.001). The individuals with GA/AA genotype of rs4846914 in Mulao had higher total cholesterol (TC) and LDL-C levels than the individuals with GG genotype in males (P < 0.05 for each). The subjects with AA genotype of rs4846914 in Han had higher LDL-C and ApoB levels, and lower HDL-C levels and the ratio of ApoA1 to ApoB than the subjects with GG genotype (P < 0.05 for each). The levels of TC in Mulao were correlated with the genotypes of rs4846914 in males (P < 0.05). The levels of ApoA1 in Han were correlated with the genotypes of both SNPs, and the levels of HDL-C and ApoB and the ratio of ApoA1 to ApoB were associated with the genotypes of rs2144300 in males (P < 0.05-0.001). The levels of LDL-C in Han were correlated with the genotypes of rs4846914 in females (P < 0.05). Serum lipid parameters were also correlated with several enviromental factors.
Conclusions: The associations of both GALNT2 rs2144300 and rs4846914 SNPs and serum lipid levels are different in the Mulao and Han populations. These discrepancies might partly result from different GALNT2 gene-enviromental interactions.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Sex-specific association of rs16996148 SNP in the NCAN/CILP2/PBX4 and serum lipid levels in the Mulao and Han populations.Lipids Health Dis. 2011 Dec 31;10:248. doi: 10.1186/1476-511X-10-248. Lipids Health Dis. 2011. PMID: 22208664 Free PMC article.
-
Association of the TRIB1 tribbles homolog 1 gene rs17321515 A>G polymorphism and serum lipid levels in the Mulao and Han populations.Lipids Health Dis. 2011 Dec 6;10:230. doi: 10.1186/1476-511X-10-230. Lipids Health Dis. 2011. PMID: 22145581 Free PMC article.
-
ATP-binding cassette transporter G5 and G8 polymorphisms and several environmental factors with serum lipid levels.PLoS One. 2012;7(5):e37972. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0037972. Epub 2012 May 24. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 22655090 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Association of the rs7395662 SNP in the MADD-FOLH1 and several environmental factors with serum lipid levels in the Mulao and Han populations.Int J Med Sci. 2013 Sep 1;10(11):1537-46. doi: 10.7150/ijms.6421. eCollection 2013. Int J Med Sci. 2013. PMID: 24046529 Free PMC article.
-
Association of the ST3GAL4 rs11220462 polymorphism and serum lipid levels in the Mulao and Han populations.Lipids Health Dis. 2014 Aug 3;13:123. doi: 10.1186/1476-511X-13-123. Lipids Health Dis. 2014. PMID: 25086711 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Genetic polymorphisms of melatonin receptors 1A and 1B may result in disordered lipid metabolism in obese patients with polycystic ovary syndrome.Mol Med Rep. 2019 Mar;19(3):2220-2230. doi: 10.3892/mmr.2019.9872. Epub 2019 Jan 17. Mol Med Rep. 2019. PMID: 30664204 Free PMC article.
-
GALNT2 rs4846914 SNP Is Associated with Obesity, Atherogenic Lipid Traits, and ANGPTL3 Plasma Level.Genes (Basel). 2022 Jul 4;13(7):1201. doi: 10.3390/genes13071201. Genes (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35885984 Free PMC article.
-
Sex-specific association of the peptidase D gene rs731839 polymorphism and serum lipid levels in the Mulao and Han populations.Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2014 Jun 15;7(7):4156-72. eCollection 2014. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2014. PMID: 25120796 Free PMC article.
-
Dissecting features of epigenetic variants underlying cardiometabolic risk using full-resolution epigenome profiling in regulatory elements.Nat Commun. 2019 Mar 14;10(1):1209. doi: 10.1038/s41467-019-09184-z. Nat Commun. 2019. PMID: 30872577 Free PMC article.
-
Common genetic variants associated with lipid profiles in a Chinese pediatric population.Hum Genet. 2013 Nov;132(11):1275-85. doi: 10.1007/s00439-013-1332-1. Epub 2013 Jul 6. Hum Genet. 2013. PMID: 23832694
References
-
- Austin MA. Plasma triglyceride as a risk factor for coronary heart disease. The epidemiologic evidence and beyond. Am J Epidemiol. 1989;129:249–59. - PubMed
-
- National Cholesterol Education Program (NCEP) Expert Panel on Detection; Treatment of High Blood Cholesterol in Adults (Adult Treatment Panel III) Third Report of the National Cholesterol Education Program (NCEP) Expert Panel on Detection, Evaluation, and Treatment of High Blood Cholesterol in Adults (Adult Treatment Panel III) final report. Circulation. 2002;106:3143–421. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

