FoxO feedback control of basal IRS-2 expression in pancreatic β-cells is distinct from that in hepatocytes
- PMID: 21933986
- PMCID: PMC3198101
- DOI: 10.2337/db11-0340
FoxO feedback control of basal IRS-2 expression in pancreatic β-cells is distinct from that in hepatocytes
Abstract
Objective: Appropriate regulation of insulin receptor substrate 2 (IRS-2) expression in pancreatic β-cells is essential to adequately compensate for insulin resistance. In liver, basal IRS-2 expression is controlled via a temporal negative feedback of sterol regulatory element-binding protein 1 (SREBP-1) to antagonize transcription factors forkhead box class O (FoxO)1/FoxO3a at an insulin response element (IRE) on the IRS-2 promoter. The purpose of the study was to examine if a similar mechanism controlled IRS-2 expression in β-cells.
Research design and methods: IRS-2 mRNA and protein expression, as well as IRS-2 gene promoter activity, were examined in isolated rat islets. Specific transcription factor association with the IRE on the IRS-2 promoter was examined by chromatin immunoprecipitation (ChIP) assay, and their nuclear translocation was examined by immunofluorescence. A direct in vivo effect of insulin on control of IRS-2 expression in liver and pancreatic islets was also investigated.
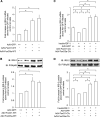
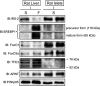
Results: In IRS-2 promoter-reporter assays conducted in isolated islets, removal of the IRE decreased basal IRS-2 promoter activity in β-cells up to 80%. Activation of IRS signaling in isolated rat islets by insulin/IGF-I (used as an experimental in vitro tool) or downstream constitutive activation of protein kinase B (PKB) significantly decreased IRS-2 expression. In contrast, inhibition of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase (PI3K) or PKB significantly increased IRS-2 levels in β-cells. ChIP assays indicated that transcription factors FoxO1 and FoxO3a associated with the IRE on the IRS-2 promoter in β-cells in a PI3K/PKB-dependent manner, whereas others, such as SREBP-1, the transcription factor binding to immunoglobulin heavy chain enhancer 3', and the aryl hydrocarbon receptor nuclear translocator (ARNT), did not. However, only FoxO3a, not FoxO1, was capable of driving IRS-2 promoter activity via the IRE in β-cells. In vivo studies showed insulin was able to suppress IRS-2 expression via activation of SREBP-1 in the liver, but this mechanism was not apparent in pancreatic islets from the same animal.
Conclusions: The molecular mechanism for feedback control of IRS signaling to decrease IRS-2 expression in liver and β-cells is quite distinct, with a predominant role played by FoxO3a in β-cells.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Specific glucose-induced control of insulin receptor substrate-2 expression is mediated via Ca2+-dependent calcineurin/NFAT signaling in primary pancreatic islet β-cells.Diabetes. 2011 Nov;60(11):2892-902. doi: 10.2337/db11-0341. Epub 2011 Sep 22. Diabetes. 2011. PMID: 21940781 Free PMC article.
-
FoxO1 inhibits sterol regulatory element-binding protein-1c (SREBP-1c) gene expression via transcription factors Sp1 and SREBP-1c.J Biol Chem. 2012 Jun 8;287(24):20132-43. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M112.347211. Epub 2012 Apr 16. J Biol Chem. 2012. PMID: 22511764 Free PMC article.
-
Nucleo-cytosolic shuttling of FoxO1 directly regulates mouse Ins2 but not Ins1 gene expression in pancreatic beta cells (MIN6).J Biol Chem. 2011 Apr 15;286(15):13647-56. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M110.204248. Epub 2011 Feb 18. J Biol Chem. 2011. PMID: 21335550 Free PMC article.
-
Diabetes outfoxed by GLP-1?Sci STKE. 2005 Jan 25;2005(268):pe2. doi: 10.1126/stke.2682005pe2. Sci STKE. 2005. PMID: 15671479 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Nuclear IRS-1 and cancer.J Cell Physiol. 2012 Aug;227(8):2992-3000. doi: 10.1002/jcp.24019. J Cell Physiol. 2012. PMID: 22454254 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
FoxO1 gain of function in the pancreas causes glucose intolerance, polycystic pancreas, and islet hypervascularization.PLoS One. 2012;7(2):e32249. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0032249. Epub 2012 Feb 23. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 22384192 Free PMC article.
-
The Paradox of Akt-mTOR Interactions.Front Oncol. 2013 Jun 20;3:165. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2013.00165. eCollection 2013. Front Oncol. 2013. PMID: 23802099 Free PMC article.
-
Phosphorylation Codes in IRS-1 and IRS-2 Are Associated with the Activation/Inhibition of Insulin Canonical Signaling Pathways.Curr Issues Mol Biol. 2024 Jan 9;46(1):634-649. doi: 10.3390/cimb46010041. Curr Issues Mol Biol. 2024. PMID: 38248343 Free PMC article. Review.
-
JNK3 maintains expression of the insulin receptor substrate 2 (IRS2) in insulin-secreting cells: functional consequences for insulin signaling.PLoS One. 2012;7(5):e35997. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0035997. Epub 2012 May 1. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 22563476 Free PMC article.
-
Endothelial TFEB (Transcription Factor EB) Improves Glucose Tolerance via Upregulation of IRS (Insulin Receptor Substrate) 1 and IRS2.Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2021 Feb;41(2):783-795. doi: 10.1161/ATVBAHA.120.315310. Epub 2020 Dec 10. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2021. PMID: 33297755 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Rhodes CJ. Type 2 diabetes-a matter of β-cell life and death? Science 2005;307:380–384 - PubMed
-
- Withers DJ, Gutierrez JS, Towery H, et al. . Disruption of IRS-2 causes type 2 diabetes in mice. Nature 1998;391:900–904 - PubMed
-
- Withers DJ, Burks DJ, Towery HH, Altamuro SL, Flint CL, White MF. Irs-2 coordinates Igf-1 receptor-mediated beta-cell development and peripheral insulin signalling. Nat Genet 1999;23:32–40 - PubMed
-
- Kubota N, Tobe K, Terauchi Y, et al. . Disruption of insulin receptor substrate 2 causes type 2 diabetes because of liver insulin resistance and lack of compensatory beta-cell hyperplasia. Diabetes 2000;49:1880–1889 - PubMed
-
- Lingohr MK, Dickson LM, Wrede CE, et al. . Decreasing IRS-2 expression in pancreatic beta-cells (INS-1) promotes apoptosis, which can be compensated for by introduction of IRS-4 expression. Mol Cell Endocrinol 2003;209:17–31 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

