Investigation of the differential potentials of TLR agonists to elicit uveitis in mice
- PMID: 21934069
- PMCID: PMC3236551
- DOI: 10.1189/jlb.0511249
Investigation of the differential potentials of TLR agonists to elicit uveitis in mice
Abstract
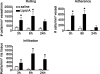
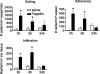
TLRs are critical for host defense and innate immunity. Emerging evidence also supports a role for TLRs in many chronic inflammatory diseases, including inflammatory eye disease, known as uveitis. The activation of TLR4 by endotoxin induces a standard model of murine uveitis. How activation of additional TLRs influences the onset and/or severity of anterior uveitis has not been examined. We sought to elucidate the potential of TLRs (TLR1/2, TLR2/6, TLR3, TLR4, TLR5, TLR7/8, and TLR9) to trigger uveitis in mice. Directly stimulated iris/ciliary body explants demonstrated a marked increase in production of inflammatory cytokines TNF-α, IL-6, IP-10/CXCL10, MCP-1, and KC with relatively little production of IFN-γ, IL-10, IL-12p40, IL-12p70, IL-17, IL-1β, IL-4, or RANTES. The cytokine-response profiles were comparable amongst the TLR agonists, albeit some differences were noted, such as greater IP-10 production following TLR3 activation. Intra-ocular injection of TLR agonists increased leukocyte interactions with the endothelium of the iris vasculature and resulted in chemotaxis into the iris tissue. Assessment of leukocytic responses by ivt videomicroscopy and histology revealed quantitative differences amongst responses to the TLR agonists with respect to the timing and numbers of rolling, adhering, iris-infiltrating, and aqueous humor-infiltrating cells, along with cytokine levels in vivo. Our data demonstrate the eye's responsiveness to a diverse array of microbial products, which activates TLRs, and reveal differences in relative cellular response among the various TLR agonists in vivo.
Figures
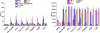



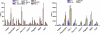
References
-
- Kawai T., Akira S. (2010) The role of pattern-recognition receptors in innate immunity: update on Toll-like receptors. Nat. Immunol. 11, 373–384 - PubMed
-
- Li M., Zhou Y., Feng G., Su S. B. (2009) The critical role of Toll-like receptor signaling pathways in the induction and progression of autoimmune diseases. Curr. Mol. Med. 9, 365–374 - PubMed
-
- Takeda K., Akira S. (2005) Toll-like receptors in innate immunity. Int. Immunol. 17, 1–14 - PubMed
-
- Assassi S., Reveille J. D., Arnett F. C., Weisman M. H., Ward M. M., Agarwal S. K., Gourh P., Bhula J., Sharif R., Sampat K., Mayes M. D., Tan F. K. (2011) Whole-blood gene expression profiling in ankylosing spondylitis shows upregulation of Toll-like receptor 4 and 5. J. Rheumatol. 38, 87–98 - PMC - PubMed
-
- Corr S. C., O'Neill L. A. (2009) Genetic variation in Toll-like receptor signalling and the risk of inflammatory and immune diseases. J. Innate Immun. 1, 350–357 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

