Evaluation of the polyclonal ELISA HPV serology assay as a biomarker for human papillomavirus exposure
- PMID: 21934576
- PMCID: PMC3178897
- DOI: 10.1097/OLQ.0b013e31822545c0
Evaluation of the polyclonal ELISA HPV serology assay as a biomarker for human papillomavirus exposure
Abstract
Background: Seropositivity to human papillomavirus (HPV)16 and 18 antibodies is used as a measure of cumulative HPV exposure and as a stratifier of HPV exposure for vaccine efficacy analyses. Overall performance of these assays, as a measure of HPV exposure, has not been evaluated.
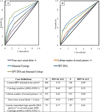
Methods: Using data from the enrollment phase of the HPV16/18 vaccine trial in Costa Rica, we evaluated the performance of the polyclonal enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) HPV16 and 18 serological assays as a measure of HPV exposure. Biologic (e.g., HPV infection at the cervix) and behavioral characteristics (e.g., lifetime number of sexual partners) with known associations with current and past HPV infection were used to define cases and controls (HPV exposed vs. not exposed). Prevaccination serum was measured for antibodies against HPV16 and 18 by ELISA; cervical samples were tested for HPV DNA using PCR SPF10/LiPA25. ELISA results were analyzed using receiver-operator characteristic curves; performance was evaluated at the manufacturer set cut point (HPV16 = 8, HPV18 = 7) and at cut points chosen to optimize sensitivity and specificity (HPV16 = 34, HPV18 = 60).
Results: Defining cases as type-specific HPV DNA positive with high-grade abnormal cytology (i.e., combined molecular and microscopic markers of infection), HPV16-ELISA gave sensitivity that was lower at the optimal cut point than the manufacturer cut point (62.2 compared with 75.7, respectively; P = 0.44). However, specificity was higher (85.3 compared with 70.4, respectively; P < 0.0001). Similarly, HPV18-ELISA gave sensitivity that was lower at the optimal cut point than the manufacturer cut point (34.5 compared with 51.7, respectively; P = 0.40), with higher specificities (94.9 compared with 72.6, respectively; P < 0.0001).
Conclusions: Modifying cut points did not improve the low sensitivity. The low sensitivity of this assay does not support its use for risk stratification or clinical settings.
Conflict of interest statement
Wim Quint and Leen-Jan van Doorn are employees of DDL Diagnostic Laboratory; Catherine Bougelet is an employee of GSK Biologicals. None of the authors have any potential conflicts of interest to report.
Figures
References
-
- Cogliano V, Baan R, Straif K, Grosse Y, Secretan B, El Ghissassi F. Carcinogenicity of human papillomaviruses. Lancet Oncol. 2005;6:204. - PubMed
-
- Dunne EF, Unger ER, Sternberg M, et al. Prevalence of HPV infection among females in the United States. JAMA. 2007;297:813–819. - PubMed
-
- Schiffman M, Herrero R, Hildesheim A, et al. HPV DNA Testing in Cervical Cancer Screening: Results from Women in a High-Risk Province in Costa Rica. JAMA. 2000;283:87–93. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

