Contrast enhanced high-resolution diffuse optical tomography of the human brain using ICG
- PMID: 21935232
- PMCID: PMC3482886
- DOI: 10.1364/OE.19.018636
Contrast enhanced high-resolution diffuse optical tomography of the human brain using ICG
Abstract
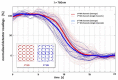
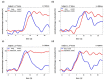
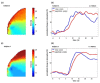
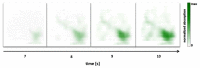
Non-invasive diffuse optical tomography (DOT) of the adult brain has recently been shown to improve the spatial resolution for functional brain imaging applications. Here we show that high-resolution (HR) DOT is also advantageous for clinical perfusion imaging using an optical contrast agent. We present the first HR-DOT results with a continuous wave near infrared spectroscopy setup using a dense grid of optical fibers and indocyanine green (ICG) as an exogenic contrast agent. We find an early arrival of the ICG bolus in the intracerebral tissue and a delayed arrival of the bolus in the extracerebral tissue, achieving the separation of both layers. This demonstrates the method's potential for brain perfusion monitoring in neurointensive care patients.
Figures


References
-
- Hopton P., Walsh T. S., Lee A., “Measurement of cerebral blood volume using near-infrared spectroscopy and indocyanine green elimination,” J. Appl. Physiol. 87(5), 1981–1987 (1999). - PubMed
-
- Keller E., Nadler A., Alkadhi H., Kollias S. S., Yonekawa Y., Niederer P., “Noninvasive measurement of regional cerebral blood flow and regional cerebral blood volume by near-infrared spectroscopy and indocyanine green dye dilution,” Neuroimage 20(2), 828–839 (2003). 10.1016/S1053-8119(03)00315-X - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

