The economic burden of TNFα inhibitors and other biologic treatments in Norway
- PMID: 21935335
- PMCID: PMC3169971
- DOI: 10.2147/CEOR.S15988
The economic burden of TNFα inhibitors and other biologic treatments in Norway
Abstract
Objective: Costly biologic therapies have improved function and quality of life for patients suffering from rheumatic and inflammatory bowel diseases. In this survey, we aimed to document and analyze the costs.
Methods: In 2008, the total costs of tumor necrosis factor alpha inhibitors and other biologic agents in Norway were registered prospectively. In addition to costs, the pattern of use in the four Norwegian health regions was analyzed. The expenses were calculated in Norwegian krone and converted into Euros.
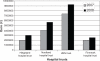
Results: The pattern of use was similar in all four regions, indicating that national guidelines are followed. Whereas the cost was similar in the southeast, western, and central regions, the expenses per thousand inhabitants were 1.56 times higher in the northern region. This indicates that patients in the northern region experienced a lower threshold for access to these drugs. The gap in costs between trusts within northern Norway was about to be closed. The Departments of Rheumatology and Gastroenterology had the highest consumption rates.
Conclusion: The total cost of biologic agents was significant. Northern Norway had among the highest consumption rates worldwide. This can partly be explained. Further exploration calls for a national registry for the use of these drugs.
Keywords: Norway; TNFα inhibitors; biologic agents; cost.
Figures

References
-
- Arentz-Hansen H, Granum L, Gulseth HC, et al. TNF Inhibitors for Rheumatic Diseases. 2006. Oslo, Norwegian Knowledge Centre for the Health Services, report 12.
-
- Arentz-Hansen H, Palm Ø, Norderhaug IN, et al. TNF Inhibitors for Rheumatic Diseases (Part 2). Effect and Side Effects. 2007. Oslo, Norwegian Knowledge Centre for the Health Services, report 2.
-
- Moen E, Neilson AR, Aaserud M, et al. TNF Inhibitors for Rheumatic Diseases (Part 3). Health Economics. 2007. Oslo, Norwegian Knowledge Centre for the Health Services, report 16. - PubMed
-
- Sæterdal I, Mørk NJ, Dalaker M, et al. TNF Inhibitors and Efalizumab for the Treatment of Skin Diseases. 2007. Oslo, Norwegian Knowledge Centre for the Health Services, report 15. - PubMed
-
- Ringerike T, Elvsaas IKØ, Coll P, et al. TNFα-inhibitors in Inflammatory Bowel Disease. 2008. Oslo, Norwegian Knowledge Centre for the Health Services, report 32. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

