Pax6 represses androgen receptor-mediated transactivation by inhibiting recruitment of the coactivator SPBP
- PMID: 21935435
- PMCID: PMC3174178
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0024659
Pax6 represses androgen receptor-mediated transactivation by inhibiting recruitment of the coactivator SPBP
Abstract
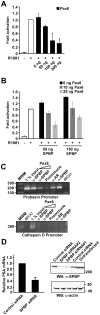
The androgen receptor (AR) has a central role in development and maintenance of the male reproductive system and in the etiology of prostate cancer. The transcription factor Pax6 has recently been reported to act as a repressor of AR and to be hypermethylated in prostate cancer cells. SPBP is a transcriptional regulator that previously has been shown to enhance the activity of Pax6. In this study we have identified SPBP to act as a transcriptional coactivator of AR. We also show that Pax6 inhibits SPBP-mediated enhancement of AR activity on the AR target gene probasin promoter, a repression that was partly reversed by increased expression of SPBP. Enhanced expression of Pax6 reduced the amount of SPBP associated with the probasin promoter when assayed by ChIP in HeLa cells. We mapped the interaction between both AR and SPBP, and AR and Pax6 to the DNA-binding domains of the involved proteins. Further binding studies revealed that Pax6 and SPBP compete for binding to AR. These results suggest that Pax6 represses AR activity by displacing and/or inhibiting recruitment of coactivators to AR target promoters. Understanding the mechanism for inhibition of AR coactivators can give rise to molecular targeted drugs for treatment of prostate cancer.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures




References
-
- Quigley CA, De Bellis A, Marschke KB, el-Awady MK, Wilson EM, et al. Androgen receptor defects: historical, clinical, and molecular perspectives. Endocr Rev. 1995;16:271–321. - PubMed
-
- Jemal A, Siegel R, Xu J, Ward E. Cancer Statistics, 2010. CA Cancer J Clin. 2010;60:277–300. - PubMed
-
- Brinkmann A, Blok LJ, de Ruiter PE, Doesburg P, Steketee K, et al. Mechanisms of androgen receptor activation and function. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol. 1999;69:307–313. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

