Novel MYH11 and ACTA2 mutations reveal a role for enhanced TGFβ signaling in FTAAD
- PMID: 21937134
- PMCID: PMC3253210
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ijcard.2011.08.079
Novel MYH11 and ACTA2 mutations reveal a role for enhanced TGFβ signaling in FTAAD
Abstract
Background: Thoracic aortic aneurysm/dissection (TAAD) is a common phenotype that may occur as an isolated manifestation or within the constellation of a defined syndrome. In contrast to syndromic TAAD, the elucidation of the genetic basis of isolated TAAD has only recently started. To date, defects have been found in genes encoding extracellular matrix proteins (fibrillin-1, FBN1; collagen type III alpha 1, COL3A1), proteins involved in transforming growth factor beta (TGFβ) signaling (TGFβ receptor 1 and 2, TGFBR1/2; and SMAD3) or proteins that build up the contractile apparatus of aortic smooth muscle cells (myosin heavy chain 11, MYH11; smooth muscle actin alpha 2, ACTA2; and MYLK).
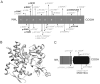
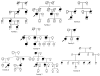
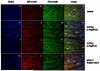
Methods and result: In 110 non-syndromic TAAD patients that previously tested negative for FBN1 or TGFBR1/2 mutations, we identified 7 ACTA2 mutations in a cohort of 43 familial TAAD patients, including 2 premature truncating mutations. Sequencing of MYH11 revealed an in frame splice-site alteration in one out of two probands with TAA(D) associated with PDA but none in the series of 22 probands from the cohort of 110 patients with non-syndromic TAAD. Interestingly, immunohistochemical staining of aortic biopsies of a patient and a family member with MYH11 and patients with ACTA2 missense mutations showed upregulation of the TGFβ signaling pathway.
Conclusions: MYH11 mutations are rare and typically identified in patients with TAAD associated with PDA. ACTA2 mutations were identified in 16% of a cohort presenting familial TAAD. Different molecular defects in TAAD may account for a different pathogenic mechanism of enhanced TGFβ signaling.
Copyright © 2011 Elsevier Ireland Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures


References
-
- Lilienfeld DE, Gunderson PD, Sprafka JM, Vargas C. Epidemiology of aortic aneurysms: I. Mortality trends in the United States, 1951 to 1981. Arteriosclerosis. 1987;7:637–43. - PubMed
-
- Milewicz DM, Michael K, Fisher N, Coselli JS, Markello T, Biddinger A. Fibrillin-1 (FBN1) mutations in patients with thoracic aortic aneurysms. Circulation. 1996;94:2708–11. - PubMed
-
- Biddinger A, Rocklin M, Coselli J, Milewicz DM. Familial thoracic aortic dilatations and dissections: a case control study. J Vasc Surg. 1997;25:506–11. - PubMed
-
- Pannu H, Fadulu VT, Chang J, et al. Mutations in transforming growth factor-beta receptor type II cause familial thoracic aortic aneurysms and dissections. Circulation. 2005;112:513–20. - PubMed
-
- Guo D, Hasham S, Kuang SQ, et al. Familial thoracic aortic aneurysms and dissections: genetic heterogeneity with a major locus mapping to 5q13-14. Circulation. 2001;103:2461–8. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

