Synchronous bilateral squamous cell carcinoma of the lung successfully treated using intensity-modulated radiotherapy
- PMID: 21937610
- PMCID: PMC3473933
- DOI: 10.1259/bjr/64570729
Synchronous bilateral squamous cell carcinoma of the lung successfully treated using intensity-modulated radiotherapy
Abstract
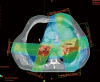
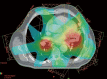
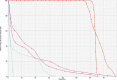
We present a case of synchronous bilateral inoperable lung cancer which required treatment with external beam radiotherapy to a radical dose. Intensity-modulated radiotherapy (IMRT) was used. More conformal dose distribution within the planning target volume was obtained using IMRT than the conventional technique. Dose-volume constraints defined for the lungs were met. Treatment was subsequently delivered using a seven-field IMRT plan. The patient remains alive and disease-free 48 months after the completion of radiotherapy. IMRT can be considered an effective treatment for synchronous bilateral lung cancer.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Conventional, conformal, and intensity-modulated radiation therapy treatment planning of external beam radiotherapy for cervical cancer: The impact of tumor regression.Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2006 Jan 1;64(1):189-96. doi: 10.1016/j.ijrobp.2005.04.025. Epub 2005 Jun 22. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2006. PMID: 15978745
-
Intensity-modulated radiotherapy for locally advanced non-small-cell lung cancer: a dose-escalation planning study.Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2011 May 1;80(1):306-13. doi: 10.1016/j.ijrobp.2010.06.025. Epub 2010 Oct 1. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2011. PMID: 20888706
-
Comparison of Toxicity Between Intensity-Modulated Radiotherapy and 3-Dimensional Conformal Radiotherapy for Locally Advanced Non-small-cell Lung Cancer.Clin Lung Cancer. 2016 Jan;17(1):18-23. doi: 10.1016/j.cllc.2015.07.006. Epub 2015 Aug 3. Clin Lung Cancer. 2016. PMID: 26303127 Free PMC article.
-
The clinical implementation of respiratory-gated intensity-modulated radiotherapy.Med Dosim. 2006 Summer;31(2):152-62. doi: 10.1016/j.meddos.2005.12.002. Med Dosim. 2006. PMID: 16690456 Review.
-
Pitfalls and Challenges to Consider before Setting up a Lung Cancer Intensity-modulated Radiotherapy Service: A Review of the Reported Clinical Experience.Clin Oncol (R Coll Radiol). 2016 Mar;28(3):185-97. doi: 10.1016/j.clon.2015.08.002. Epub 2015 Aug 29. Clin Oncol (R Coll Radiol). 2016. PMID: 26329504 Review.
Cited by
-
Dosimetric and biological comparisons of single planning and double plannings for bilateral lung cancer SBRT planning based on the Cyber-Knife system.Front Oncol. 2022 Nov 21;12:1015999. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2022.1015999. eCollection 2022. Front Oncol. 2022. PMID: 36483053 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Beyreuther H. Multiplicitat von carcinomen bei ein fall von sog: ‘schneeberger’ lungenkrebs mit tuberculose. Virchows Arch Pathol Anat 1924;250:230–6
-
- Trousse D, Barlesi F, Loundou A, Tasei AM, Doddoli C, Giudicell R, et al. Synchronous multiple primary lung cancer: An increasing clinical occurrence requiring multidisciplinary management. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg 2007;133:1193–200 - PubMed
-
- Martini N, Melamed MR. Multiple primary lung cancers. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg 1975;70:606–12 - PubMed
-
- Postmus P, Brambilla E, Chansky K, Crowley J, Goldstraw P, Patz EF, Jr, et al. The IASLC lung cancer staging project: proposals for revision of the M descriptors in the forthcoming (seventh) edition of the TNM classification of lung cancer. J Thorac Oncol 2007;2:686–93 - PubMed
-
- Goldstraw P, Crowley J, Chansky K, Giroux DJ, Groome PA, Rami-Porta R, et al. The IASLC lung cancer staging project: proposals for the revision of the TNM stage groupings in the forthcoming (seventh) edition of the TNM classification of malignant tumours. J Thorac Oncol 2007;2:706–14 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

