Effective dose delivered by conventional radiology to Aosta Valley population between 2002 and 2009
- PMID: 21937611
- PMCID: PMC3474076
- DOI: 10.1259/bjr/19099861
Effective dose delivered by conventional radiology to Aosta Valley population between 2002 and 2009
Abstract
Objective: Medical diagnostic procedures can be considered the main man-made source of ionising radiation exposure for the population. Conventional radiography still represents the largest contribution to examination frequency. The present work evaluates procedure frequency and effective dose from the majority of conventional radiology examinations performed at the Radiological Department of Aosta Hospital from 2002 to 2009.
Method: Effective dose to the patient was evaluated by means of the software PCXMC. Data provided by the radiological information system allowed us to obtain collective effective and per caput dose.
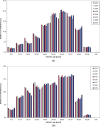
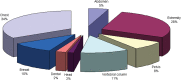
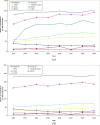
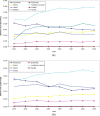
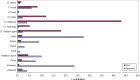
Results: The biggest contributors to per caput effective dose from conventional radiology are vertebral column, abdomen, chest, pelvis and (limited to females) breast. Vertebral column, pelvis and breast procedures show a significant dose increment in the period of the study. The mean effective dose per inhabitant from conventional radiology increased from 0.131 mSv in 2002 to 0.156 mSv in 2009. Combining these figures with those from our study of effective dose from CT (0.55 mSv in 2002 to 1.03 mSv in 2009), the total mean effective dose per inhabitant increased from 0.68 mSv to 1.19 mSv. The contribution of CT increased from 81% to 87% of the total. In contrast, conventional radiology accounts for 85% of the total number of procedures, but only 13% of the effective dose.
Conclusion: The study has demonstrated that conventional radiography still represents the biggest contributor to examination frequency in Aosta Valley in 2009. However, the frequency of the main procedures did not change significantly between 2002 and 2009.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Population exposure to ionising radiation from CT examinations in Aosta Valley between 2001 and 2008.Br J Radiol. 2010 Dec;83(996):1042-51. doi: 10.1259/bjr/66718758. Br J Radiol. 2010. PMID: 21088089 Free PMC article.
-
Population exposure to ionizing radiation from medical examinations in France.Br J Radiol. 2008 Mar;81(963):204-13. doi: 10.1259/bjr/24344062. Br J Radiol. 2008. PMID: 18270294
-
Diagnostic radiology in Norway trends in examination frequency and collective effective dose.Radiat Prot Dosimetry. 2007;124(4):339-47. doi: 10.1093/rpd/ncm204. Epub 2007 May 25. Radiat Prot Dosimetry. 2007. PMID: 17526908
-
Medical exposure to radiation and thyroid cancer.Clin Oncol (R Coll Radiol). 2011 May;23(4):244-50. doi: 10.1016/j.clon.2011.01.159. Epub 2011 Feb 5. Clin Oncol (R Coll Radiol). 2011. PMID: 21296564 Review.
-
Exposure of the Swiss population by medical x-rays: 2008 review.Health Phys. 2012 Mar;102(3):263-70. doi: 10.1097/hp.0b013e31823513ff. Health Phys. 2012. PMID: 22420018 Review.
Cited by
-
European Guidelines for AP/PA chest X-rays: routinely satisfiable in a paediatric radiology division?Eur Radiol. 2016 Feb;26(2):495-505. doi: 10.1007/s00330-015-3836-7. Epub 2015 May 24. Eur Radiol. 2016. PMID: 26002133
-
Analysis of dose monitoring for external exposure to radiology in hospital workers from 2010 to 2018.Am J Transl Res. 2021 Apr 15;13(4):3357-3362. eCollection 2021. Am J Transl Res. 2021. PMID: 34017510 Free PMC article.
-
Image quality is resilient against tube voltage variations in post-mortem skeletal radiography with a digital flat-panel detector.Sci Rep. 2021 Apr 8;11(1):7701. doi: 10.1038/s41598-021-87294-9. Sci Rep. 2021. PMID: 33833315 Free PMC article.
-
Advances in multiscale image processing and its effects on image quality in skeletal radiography.Sci Rep. 2022 Mar 18;12(1):4726. doi: 10.1038/s41598-022-08699-8. Sci Rep. 2022. PMID: 35304544 Free PMC article.
-
The contribution of interventional cardiology procedures to the population radiation dose in a 'health-care level I' representative region.Radiat Prot Dosimetry. 2016 Feb;168(2):261-70. doi: 10.1093/rpd/ncv307. Epub 2015 May 25. Radiat Prot Dosimetry. 2016. PMID: 26012484 Free PMC article.
References
-
- United NationsScientificCommitteeontheEffectsofAtomicRadiation(UNSCEAR) Sources and effects of ionizing radiation. New York, NY: United Nations; 2000
-
- Havukainen R, Pirinen M. Patient dose and image quality in five standard X-ray examinations. Med Phys 1993;20:813–17 - PubMed
-
- Gray JE, Archer BR, Butler PF, Hobbs BB, Mettler FA, Pizzutiello RJ, et al. Reference values for diagnostic radiology: application and impact. Radiology 2005;235:354–8 - PubMed
-
- Børretzen I, Lysdahl KB, Olerud HM. Diagnostic radiology in Norway—trends in examination frequency and collective effective dose. Rad Pro Dos 2007;124:339–47 - PubMed
-
- Scanff P, Donadieu J, Pirard P, Aubert B. Population exposure to ionizing radiation from medical examinations in France. Br J Radiol 2008;81:204–13 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

