Immunopathogenic and antibacterial effects of H3N2 influenza A virus PB1-F2 map to amino acid residues 62, 75, 79, and 82
- PMID: 21937639
- PMCID: PMC3209399
- DOI: 10.1128/JVI.05872-11
Immunopathogenic and antibacterial effects of H3N2 influenza A virus PB1-F2 map to amino acid residues 62, 75, 79, and 82
Abstract
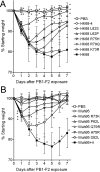
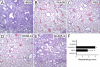
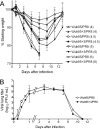
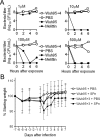
The influenza A virus protein PB1-F2 has been linked to the pathogenesis of both primary viral and secondary bacterial infections. H3N2 viruses have historically expressed full-length PB1-F2 proteins with either proinflammatory (e.g., from influenza A/Hong Kong/1/1968 virus) or noninflammatory (e.g., from influenza A/Wuhan/359/1995 virus) properties. Using synthetic peptides derived from the active C-terminal portion of the PB1-F2 protein from those two viruses, we mapped the proinflammatory domain to amino acid residues L62, R75, R79, and L82 and then determined the role of that domain in H3N2 influenza virus pathogenicity. PB1-F2-derived peptides containing that proinflammatory motif caused significant morbidity, mortality, and pulmonary inflammation in mice, manifesting as increased acute lung injury and the presence of proinflammatory cytokines and inflammatory cells in the lungs compared to peptides lacking this motif, and better supported bacterial infection with Streptococcus pneumoniae. Infections of mice with an otherwise isogenic virus engineered to contain this proinflammatory sequence in PB1-F2 demonstrated increased morbidity resulting from primary viral infections and enhanced development of secondary bacterial pneumonia. The presence of the PB1-F2 noninflammatory (P62, H75, Q79, and S82) sequence in the wild-type virus mediated an antibacterial effect. These data suggest that loss of the inflammatory PB1-F2 phenotype that supports bacterial superinfection during adaptation of H3N2 viruses to humans, coupled with acquisition of antibacterial activity, contributes to the relatively diminished frequency of severe infections seen with seasonal H3N2 influenza viruses in recent decades compared to their first 2 decades of circulation.
Figures
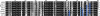


References
-
- Bruns K., et al. 2007. Structural characterization and oligomerization of PB1-F2, a proapoptotic influenza A virus protein. J. Biol. Chem. 282:353–363 - PubMed
-
- Chen W., et al. 2001. A novel influenza A virus mitochondrial protein that induces cell death. Nat. Med. 7:1306–1312 - PubMed
-
- Collins S. D. 1932. Excess mortality from causes other than influenza and pneumonia during influenza epidemics. Public Health Rep. 47:2159–2179 - PubMed
-
- Condit R. C. 2007. Virus cultivation, detection, and genetics, p. 25–57 In Flint S. J., Enquist L. W., Krug R. M., Racaniello V. R., Skarzynski T. (ed.), Principles of virology: molecular biology, pathogenesis, and control of animal viruses. ASM Press, Washington, DC
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

