Automatic detection of fast oscillations (40-200 Hz) in scalp EEG recordings
- PMID: 21940200
- PMCID: PMC3774655
- DOI: 10.1016/j.clinph.2011.07.050
Automatic detection of fast oscillations (40-200 Hz) in scalp EEG recordings
Abstract
Objective: We aim to automatically detect fast oscillations (40-200 Hz) related to epilepsy on scalp EEG recordings.
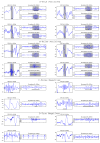
Methods: The detector first finds localized increments of the signal power in narrow frequency bands. A simple classification based on two features, a narrowband to wideband signal amplitude ratio and an absolute narrowband signal amplitude, then allows for an important reduction in the number of false positives.
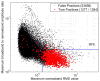
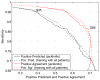
Results: When compared to an expert, the performance in 15 focal epilepsy patients resulted in 3.6 false positives per minute at 95% sensitivity, with at least 40% of the detected events being true positives. In most of the patients the channels showing the highest number of events according to the expert and the automatic detector were the same.
Conclusions: A high sensitivity is achieved with the proposed automatic detector, but results should be reviewed by an expert to remove false positives.
Significance: The time required to mark fast oscillations on scalp EEG recordings is drastically reduced with the use of the proposed detector. Thus, the automatic detector is a useful tool in studies aiming to create a better understanding of the fast oscillations visible on the scalp.
Copyright © 2011 International Federation of Clinical Neurophysiology. Published by Elsevier Ireland Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures
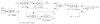
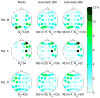
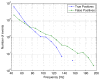
Comment in
-
EEG in the 21st century: moving into the fast lane?Clin Neurophysiol. 2012 Apr;123(4):630. doi: 10.1016/j.clinph.2011.08.018. Epub 2011 Sep 21. Clin Neurophysiol. 2012. PMID: 21940202 No abstract available.
References
-
- Aarabi A, Grebe R, Wallois F. A multistage knowledge-based system for EEG seizure detection in newborn infants. Clin Neurophysiol. 2007;118:2781–97. - PubMed
-
- Bragin A, Engel J, Jr, Wilson CL, Fried I, Mathern GW. Hippocampal and entorhinal cortex high-frequency oscillations (100–500 Hz) in human epileptic brain and in kainic acid-treated rats with chronic seizures. Epilepsia. 1999a;40:127–37. - PubMed
-
- Bragin A, Engel J, Jr, Wilson CL, Vizentin E, Mathern GW. Electrophysiologic analysis of a chronic seizure model after unilateral hippocampal KA injection. Epilepsia. 1999b;40:1210–21. - PubMed
-
- Bragin A, Engel J, Jr, Wilson CL, Fried I, Buzsaki G. High frequency oscillations in human brain. Hippocampus. 1999b;9:137–42. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

